The Effect of Q Angle and Hamstring Length on Balance Performance in Gonarthrosis Patients
- PMID: 37719611
- PMCID: PMC10504572
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.43615
The Effect of Q Angle and Hamstring Length on Balance Performance in Gonarthrosis Patients
Abstract
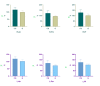
Introduction Gonarthrosis (G) is a progressive disease that affects the knee joint and causes pain and limitation of movement in the knee. The determination of the morphometric status of G patients has been a subject of interest recently. The purpose of this study is to determine how hamstring length (HL) and patellofemoral angle (Q angle [QA]) affect the ability of individuals with G to maintain balance. Methods A total of 80 (40 G patients and 40 in the control group [CG]) participants aged 40-65 were included in the study. A goniometer was used to measure the participants' QA. The mean age of the participants was 50.18±7.16 in the G group and 51.40±6.64 in CG. HL was measured using the sit-and-reach test. Participants' dynamic balance state was evaluated using the Y balance test by stepping in the following directions: right-anterior (R-An), right-posteromedial (R-Pm), right-posterolateral (R-Pl), left-anterior (L-An), left-posteromedial (L-Pm), and left-posterolateral (L-Pl). Results According to the results of this research, the balance performance of G patients was significantly lower in all directions (R-An, R-Pm, R-Pl, L-An, L-Pm, L-Pl) compared to the CG. In both groups, R-QA, L-QA, and HL did not change. However, linear regression analysis indicated that in G patients, R-QA, L-QA, and HL affected balance performance. No significant interaction was found between these parameters and balance performance in the CG. Conclusion HL and QA have a significant role in determining body balance. In our study, we found that QA decreased in G patients, leading to genu varum in these individuals. The hamstring muscle shortening observed in G patients significantly negatively affected balance, especially in the R-An, R-Pm, L-An, L-Pm, and L-Pl directions. For healthcare professionals preparing treatment protocols for G patients, we recommend providing exercises to improve balance, especially in these directions.
Keywords: balance; control group; gonarthrosis; hamstring length; q angle.
Copyright © 2023, Ciftci et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between core stability and dynamic balance in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis.Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2017 Oct 6;64(3):239-245. doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2018.1674. eCollection 2018 Sep. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 31453517 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of quadriceps angle on static and dynamic balance in young adults.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2019;32(6):857-862. doi: 10.3233/BMR-181332. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 30932878
-
Modeling the effect of static stretching and strengthening exercise in lengthened position on balance in low back pain subject with shortened hamstring: a randomized controlled clinical trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Dec 4;21(1):809. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03823-z. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 33276764 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The relationship between performance on the modified star excursion balance test and the knee muscle strength before and after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Knee. 2018 Aug;25(4):588-594. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2018.05.010. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Knee. 2018. PMID: 29886009
-
Kinematic analysis of selected reach directions of the Star Excursion Balance Test compared with the Y-Balance Test.J Sport Rehabil. 2014 Feb;23(1):27-35. doi: 10.1123/jsr.2012-0114. Epub 2013 Aug 12. J Sport Rehabil. 2014. PMID: 23945793
References
-
- Osteoarthritis 1991. Current drug treatment regimens. Al Arfag A, Davis P. Drugs. 1991;41:193–201. - PubMed
-
- The prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the elderly. The Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Felson DT, Naimark A, Anderson J, Kazis L, Castelli W, Meenan RF. Arthritis Rheum. 1987;30:914–918. - PubMed
-
- Evidence-based health policy--lessons from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Science. 1996;274:740–743. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
