Development and Validation of Questionnaire to Measure Parents' Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice on Self-Medication of Children with Antibiotics in Bandung, Indonesia
- PMID: 37719655
- PMCID: PMC10505016
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S426313
Development and Validation of Questionnaire to Measure Parents' Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice on Self-Medication of Children with Antibiotics in Bandung, Indonesia
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to develop and validate a questionnaire to measure the knowledge, attitude, and practice of parents regarding antibiotic use in Indonesian children using structural equation modeling (SEM) analysis.
Methods: The instrument development process was conducted from January 5 to 19, 2023, using the following steps: 1) literature review and item development, 2) internal review and refinement, 3) structural model analysis, and 4) measurement models' reliability and validity. A convenience sample was used to recruit parents as participants from Arcamanik District, Bandung, Indonesia. A total of 83 respondents completed the on-site interview questionnaire. Furthermore, statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Version 21.0 and Analysis of Moment Structures (AMOS) Version 26.0.
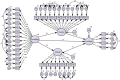
Results: The content validity for the scales was over 50%, and the reliabilities for the 38 items of the questionnaire were above 0.6, respectively. The suitability of the model was assessed, and the findings showed parameters for indicators: chi-square = 0.0004, CFI = 0.977, RMSEA = 0.044, CMIN/DF = 1.162, AGFI = 0.651, TLI = 0.973, and NFI = 0.860. The GFI parameter did not fit with the output value of 0.718, while the convergent and divergent validity of scores provided evidence in the expected direction.
Conclusion: This psychometric development study provides preliminary evidence that the 38-item scales were reliable and valid for assessing knowledge, attitude, and practice toward parents in the self-medication of antibiotics in children.
Keywords: children; drug resistance; parents; reliability; structural equation modeling; validity.
© 2023 Pitaloka et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and validation of traditional & complementary medicine (TCM) scales for nurses: Using structural equation modelling (SEM).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 21;19(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2733-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31752832 Free PMC article.
-
Using Social Media Platforms to Raise Health Awareness and Increase Health Education in Pakistan: Structural Equation Modeling Analysis and Questionnaire Study.JMIR Hum Factors. 2025 Apr 7;12:e65745. doi: 10.2196/65745. JMIR Hum Factors. 2025. PMID: 40194316 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of the Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Questionnaire for Community Pharmacy Personnel in Tuberculosis Case Detection, Drug Monitoring, and Education: A Study from Indonesia.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Jun 13;16:3729-3741. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S409107. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37333684 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of the Indonesian version of the nursing home survey on patient safety culture.Int J Older People Nurs. 2023 Sep;18(5):e12553. doi: 10.1111/opn.12553. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Int J Older People Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37334471
-
Development and validation of parental knowledge, attitude and practice in eye problem among children questionnaire (PEPC-KAPQ).PLoS One. 2023 Sep 8;18(9):e0291062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291062. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37682886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cassini A, Högberg LD, Plachouras D, et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):56–66. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous