Development of a novel, clinically relevant anoikis-related gene signature to forecast prognosis in patients with prostate cancer
- PMID: 37719710
- PMCID: PMC10499615
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1166668
Development of a novel, clinically relevant anoikis-related gene signature to forecast prognosis in patients with prostate cancer
Abstract
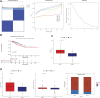
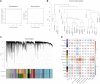
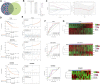
Introduction: Anoikis is a specific form of programmed cell death and is related to prostate cancer (PC) metastasis. This study aimed to develop a reliable anoikis-related gene signature to accurately forecast PC prognosis. Methods: Based on anoikis-related genes and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data, anoikis-related molecular subtypes were identified, and their differences in disease-free survival (DFS), stemness, clinical features, and immune infiltration patterns were compared. Differential expression analysis of the two subtypes and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were employed to identify clinically relevant anoikis-related differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between subtypes, which were then selected to construct a prognostic signature. The clinical utility of the signature was verified using the validation datasets GSE116918 and GSE46602. A nomogram was established to predict patient survival. Finally, differentially enriched hallmark gene sets were revealed between the different risk groups. Results: Two anoikis-related molecular subtypes were identified, and cluster 1 had poor prognosis, higher stemness, advanced clinical features, and differential immune cell infiltration. Next, 13 clinically relevant anoikis-related DEGs were identified, and five of them (CKS2, CDC20, FMOD, CD38, and MSMB) were selected to build a prognostic signature. This gene signature had a high prognostic value. A nomogram that combined Gleason score, T stage, and risk score could accurately predict patient survival. Furthermore, gene sets closely related with DNA repair were differentially expressed in the different risk groups. Conclusion: A novel, clinically relevant five-anoikis-related gene signature was a powerful prognostic biomarker for PC.
Keywords: anoikis; gene signature; prognosis; prostate cancer; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis and experimental verification of the mechanism of anoikis related genes in pancreatic cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 13;10(16):e36234. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36234. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39253230 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of the Anoikis-Related Gene Signature as a Novel Prognostic Model for Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Endocervical Adenocarcinoma, and Revelation Immune Infiltration.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Feb 13;59(2):358. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020358. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36837559 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel anoikis-related gene signature to predict prognosis and tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Jan;14(3):320-330. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14766. Epub 2022 Dec 11. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36507553 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the prognostic value in lung adenocarcinoma based on anoikis-related genes and initial experimental validation.J Gene Med. 2023 Sep;25(9):e3534. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3534. Epub 2023 May 31. J Gene Med. 2023. PMID: 37259225
-
An anoikis-related gene signature predicts prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and immunotherapy.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 15;14(11):5116-5132. doi: 10.62347/MJTA2660. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39659934 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of regulatory T cells specific genes predictive models of prostate cancer patients based on machine learning: a computational analysis and in vitro experiments.Discov Oncol. 2025 Feb 13;16(1):178. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01862-3. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39948230 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenesis-related gene signature for prognostic prediction and immune microenvironment characterization in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Apr 8;25(1):108. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01628-9. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40198448 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological characterization and prognostic of colon cancer evaluated by angiogenesis-related features: a computational analysis and in vitro experiments.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jan 29;16(1):101. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01835-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39881026 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering somatic genetic drivers in prostate cancer through comprehensive genome-wide analysis.Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):5039-5056. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01623-8. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40156736 Free PMC article.
-
Biological functions and therapeutic potential of CKS2 in human cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 12;14:1424569. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1424569. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39188686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Qattan M. M., Al-Qattan A. M. (2018). Fibromodulin: structure, physiological functions, and an emphasis on its potential clinical applications in various diseases. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak 28 (28), 783–790. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

