Novel biomarkers used for early diagnosis and tyrosine kinase inhibitors as targeted therapies in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 37719843
- PMCID: PMC10502318
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1189799
Novel biomarkers used for early diagnosis and tyrosine kinase inhibitors as targeted therapies in colorectal cancer
Abstract
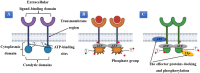
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common and second most lethal type of cancer worldwide, presenting major health risks as well as economic costs to both people and society. CRC survival chances are significantly higher if the cancer is diagnosed and treated early. With the development of molecular biology, numerous initiatives have been undertaken to identify novel biomarkers for the early diagnosis of CRC. Pathological disorders can be diagnosed at a lower cost with the help of biomarkers, which can be detected in stool, blood, and tissue samples. Several lines of evidence suggest that the gut microbiota could be used as a biomarker for CRC screening and treatment. CRC treatment choices include surgical resection, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, gene therapy, and combination therapies. Targeted therapies are a relatively new and promising modality of treatment that has been shown to increase patients' overall survival (OS) rates and can inhibit cancer cell development. Several small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are being investigated as potential treatments due to our increasing awareness of CRC's molecular causes and oncogenic signaling. These compounds may inhibit critical enzymes in controlling signaling pathways, which are crucial for CRC cells' development, differentiation, proliferation, and survival. On the other hand, only one of the approximately 42 TKIs that demonstrated anti-tumor effects in pre-clinical studies has been licensed for clinical usage in CRC. A significant knowledge gap exists when bringing these tailored medicines into the clinic. As a result, the emphasis of this review is placed on recently discovered biomarkers for early diagnosis as well as tyrosine kinase inhibitors as possible therapy options for CRC.
Keywords: biomarker; colorectal cancer; diagnosis; therapies; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2023 Jiang, Zhou and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adnan M., Koli S., Mohammad T., Siddiqui A. J., Patel M., Alshammari N., et al. (2022). Searching for novel anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors: structure-guided screening of natural compounds for a tyrosine kinase therapeutic target in cancers. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 26 (8), 461–470. 10.1089/omi.2022.0067 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmed F. E., Gouda M. M., Ahmed N. C., Hussein L. (2019). Quantification of microRNAs by absolute Dpcr for the diagnostic screening of colon cancer. J. Colon Rectal Cancer 1 (3), 10–37. 10.14302/issn.2471-7061.jcrc-18-2526 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous