Distinct Types of Cell Death and Implications in Liver Diseases: An Overview of Mechanisms and Application
- PMID: 37719956
- PMCID: PMC10500292
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00132
Distinct Types of Cell Death and Implications in Liver Diseases: An Overview of Mechanisms and Application
Abstract
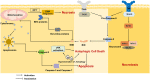
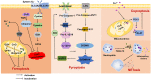
Cell death is associated with a variety of liver diseases, and hepatocyte death is a core factor in the occurrence and progression of liver diseases. In recent years, new cell death modes have been identified, and certain biomarkers have been detected in the circulation during various cell death modes that mediate liver injury. In this review, cell death modes associated with liver diseases are summarized, including some cell death modes that have emerged in recent years. We described the mechanisms associated with liver diseases and summarized recent applications of targeting cell death in liver diseases. It provides new ideas for the diagnosis and treatment of liver diseases. In addition, multiple cell death modes can contribute to the same liver disease. Different cell death modes are not isolated, and they interact with each other in liver diseases. Future studies may focus on exploring the regulation between various cell death response pathways in liver diseases.
Keywords: Application; Cell death; Hepatocytes; Liver diseases.
© 2023 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
References
-
- Yan G, Elbadawi M, Efferth T. Multiple cell death modalities and their key features (Review) World Acad Sci J. 2020;2(2):39–48. doi: 10.3892/wasj.2020.40. - DOI
-
- Heidelbaugh JJ, Bruderly M. Cirrhosis and chronic liver failure: part I. Diagnosis and evaluation. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(5):756–762. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
