This is a preprint.
Live imaging of the airway epithelium reveals that mucociliary clearance modulates SARS-CoV-2 spread
- PMID: 37720034
- PMCID: PMC10503848
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3246773/v1
Live imaging of the airway epithelium reveals that mucociliary clearance modulates SARS-CoV-2 spread
Update in
-
Live imaging of airway epithelium reveals that mucociliary clearance modulates SARS-CoV-2 spread.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 2;15(1):9480. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53791-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39488529 Free PMC article.
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 initiates infection in the conducting airways, which rely on mucocilliary clearance (MCC) to minimize pathogen penetration. However, it is unclear how MCC impacts SARS-CoV-2 spread after infection is established. To understand viral spread at this site, we performed live imaging of SARS-CoV-2 infected differentiated primary human bronchial epithelium cultures for up to 9 days. Fluorescent markers for cilia and mucus allowed longitudinal monitoring of MCC, ciliary motion, and infection. The number of infected cells peaked at 4 days post-infection in characteristic foci that followed mucus movement. Inhibition of MCC using physical and genetic perturbations limited foci. Later in infection, MCC was diminished despite relatively subtle ciliary function defects. Resumption of MCC and infection spread after mucus removal suggests that mucus secretion mediates this effect. We show that MCC facilitates SARS-CoV-2 spread early in infection while later decreases in MCC inhibit spread, suggesting a complex interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and MCC.
Keywords: airway; airway epithelial cells; cilia; epithelium; innate immunity; live cell imaging; microscopy; mucociliary clearance; mucus; respiratory virus; sars-cov-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS J.F.H. has received research support, paid to Northwestern University, from Gilead Sciences and is a paid consultant for Merck. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


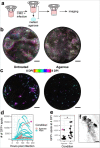
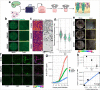
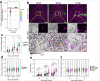
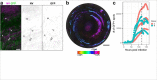
References
-
- Killingley B. et al. Safety, tolerability and viral kinetics during SARS-CoV-2 human challenge in young adults. Nat. Med. 28, 1031–1041 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

