Spinal TAOK2 contributes to neuropathic pain via cGAS-STING activation in rats
- PMID: 37720090
- PMCID: PMC10502416
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107792
Spinal TAOK2 contributes to neuropathic pain via cGAS-STING activation in rats
Abstract
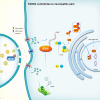
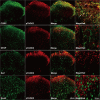
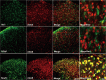
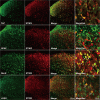
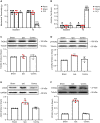
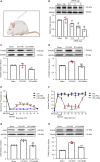
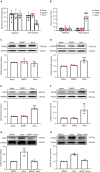
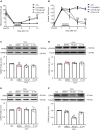
Thousand and one amino acid kinase 2 (TAOK2) is a member of the mammalian sterile 20 kinase family and is implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders; however, its role in neuropathic pain remains unknown. Here, we found that TAOK2 was enriched and activated after chronic constriction injury (CCI) in the rat spinal dorsal horn. Meanwhile, cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling was also activated with hyperalgesia. Silencing TAOK2 reversed hyperalgesia and suppressed the activation of cGAS-STING signaling induced by CCI, while pharmacological activation of TAOK2 induced pain hypersensitivity and upregulation of cGAS-STING signaling in naive rats. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition or gene silencing of cGAS-STING signaling attenuated CCI-induced hyperalgesia. Taken together, these data demonstrate that the activation of spinal TAOK2 contributes to CCI-induced hyperalgesia via cGAS-STING signaling activation, providing new molecular targets for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Cell biology; Molecular biology; Neuroscience.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological inhibition of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway suppresses microglial M1-polarization in the spinal cord and attenuates neuropathic pain.Neuropharmacology. 2022 Oct 1;217:109206. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109206. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35926582
-
Activation of mitochondrial DNA-mediated cGAS-STING pathway contributes to chronic postsurgical pain by inducing type I interferons and A1 reactive astrocytes in the spinal cord.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Jan 25;127:111348. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111348. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38086268
-
The cGAS-STING signaling in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: Future novel target option for pharmacotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):50-75. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 May 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological targeting of cGAS/STING-YAP axis suppresses pathological angiogenesis and ameliorates organ fibrosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 15;932:175241. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175241. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36058291
-
The role of cGAS-STING signalling in liver diseases.JHEP Rep. 2021 Jun 24;3(5):100324. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100324. eCollection 2021 Oct. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vinorelbine causes a neuropathic pain-like state in mice via STING and MNK1 signaling associated with type I interferon induction.iScience. 2024 Jan 8;27(2):108808. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108808. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38303713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finnerup N.B., Haroutounian S., Kamerman P., Baron R., Bennett D.L.H., Bouhassira D., Cruccu G., Freeman R., Hansson P., Nurmikko T., et al. Neuropathic pain: an updated grading system for research and clinical practice. Pain. 2016;157:1599–1606. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa T., Murata K., Okuda H., Potapenko I., Hori K., Furuyama T., Yamamoto R., Ono M., Kato N., Fukazawa Y., Ozaki N. Pain-related neuronal ensembles in the primary somatosensory cortex contribute to hyperalgesia and anxiety. iScience. 2023;26 doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106332. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

