A Case Report of Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block Relieving Chronic Pain Post-Dental Bone Graft Surgery
- PMID: 37720120
- PMCID: PMC10504432
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.45266
A Case Report of Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block Relieving Chronic Pain Post-Dental Bone Graft Surgery
Abstract
Chronic orofacial pain, by definition, is a pain that can anatomically extend anywhere between the area just under the orbitomeatal line, anterior to the pinnae, and above the neck. It occurs for 15 days or more per month, lasting four or more hours daily, for at least three months. Chronic orofacial pain, including persistent idiopathic facial pain syndrome, can significantly impact patients' quality of life and pose challenges for effective management. This case report describes a successful transnasal approach in treating a patient with severe oral pain following a bone graft surgery by blocking the sphenopalatine ganglion. The block provided significant pain relief and improved the patient's daily functioning. This minimally invasive treatment option offers an alternative for managing chronic orofacial pain after dental procedures such as bone graft surgery.
Keywords: bone graft; chronic pain; orofacial pain; persistent idiopathic facial pain syndrome; sphenopalatine ganglion block.
Copyright © 2023, Levin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
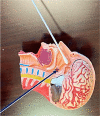
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel revision to the classical transnasal topical sphenopalatine ganglion block for the treatment of headache and facial pain.Pain Physician. 2013 Nov-Dec;16(6):E769-78. Pain Physician. 2013. PMID: 24284858
-
[Ropivacaine use in transnasal sphenopalatine ganglion block for post dural puncture headache in obstetric patients - case series].Braz J Anesthesiol. 2018 Jul-Aug;68(4):421-424. doi: 10.1016/j.bjan.2017.11.007. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 29402441 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Transnasal Versus Ultrasound-Guided Suprazygomatic Approaches for Sphenopalatine Ganglion Blocks in Persistent Idiopathic Facial Pain.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2025 Mar 1;28(2):189-195. doi: 10.4103/aian.aian_713_24. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40087987 Free PMC article.
-
Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block in the Management of Chronic Headaches.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017 Jun;21(6):27. doi: 10.1007/s11916-017-0626-8. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2017. PMID: 28432602 Review.
-
Perioperative local anaesthesia for reducing pain following septal surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 23;8(8):CD012047. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012047.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30136717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Estimated prevalence and distribution of reported orofacial pain in the United States. Lipton JA, Ship JA, Larach-Robinson D. J Am Dent Assoc. 1993;124:115–121. - PubMed
-
- Persistent idiopathic facial pain. Benoliel R, Gaul C. Cephalalgia. 2017;37:680–691. - PubMed
-
- Topical sphenopalatine ganglion block compared with epidural blood patch for postdural puncture headache management in postpartum patients: a retrospective review. Cohen S, Levin D, Mellender S, Zhao R, Patel P, Grubb W, Kiss G. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018;43:880–884. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
