Diabetic Ketoacidosis-Induced "Terrible Triad" Associated With Seizures and Acute Renal Failure: A Report of a Rare Case
- PMID: 37720132
- PMCID: PMC10500620
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.45214
Diabetic Ketoacidosis-Induced "Terrible Triad" Associated With Seizures and Acute Renal Failure: A Report of a Rare Case
Abstract
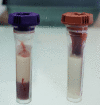
We report a case of a 17-year-old male patient who came to the emergency department with abdominal pain, headaches for two days, lethargy, and Kussmaul breathing. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was diagnosed. The patient's clinical course was complicated with a severely elevated triglyceride (TG) level (25,585 mg/dL), acute pancreatitis, renal involvement, and generalized seizures. The proposed mechanism is triglyceride excess due to increased lipolysis, resulting in the formation of excess free fatty acids. The objective of this case report is to present and describe the clinical features, laboratory investigations, case management, and natural course of hypertriglyceridemia in DKA.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; diabetes mellitus; diabetic ketoacidosis; hypertriglyceridemia; seizures; terrible triad of endocrinology.
Copyright © 2023, Kavathia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes mellitus: diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Kitabchi AE, Nyenwe EA. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2006;35:725-51, viii. - PubMed
-
- Insulin and type 1 diabetes: immune connections. Culina S, Brezar V, Mallone R. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013;168:0–31. - PubMed
-
- Loscalzo J, Fauci A, Kasper D, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson JL. 21st edition. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill; 2022. Harrison's principles of internal medicine, 21st edition.
-
- Clinical assessment of hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. Fortson MR, Freedman SN, Webster PD 3rd. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8540502/ Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:2134–2139. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous