Sigma-1 receptor knockout disturbs gut microbiota, remodels serum metabolome, and exacerbates isoprenaline-induced heart failure
- PMID: 37720144
- PMCID: PMC10501138
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1255971
Sigma-1 receptor knockout disturbs gut microbiota, remodels serum metabolome, and exacerbates isoprenaline-induced heart failure
Abstract
Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is usually the end stage of the continuum of various cardiovascular diseases. However, the mechanism underlying the progression and development of HF remains poorly understood. The sigma-1 receptor (Sigmar1) is a non-opioid transmembrane receptor implicated in many diseases, including HF. However, the role of Sigmar1 in HF has not been fully elucidated.
Methods: In this study, we used isoproterenol (ISO) to induce HF in wild-type (WT) and Sigmar1 knockout (Sigmar1-/-) mice. Multi-omic analysis, including microbiomics, metabolomics and transcriptomics, was employed to comprehensively evaluate the role of Sigmar1 in HF.
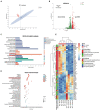
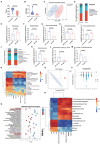
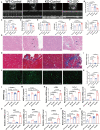
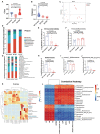
Results: Compared with the WT-ISO group, Sigmar1-/- aggravated ISO-induced HF, including left ventricular systolic dysfunction and ventricular remodeling. Moreover, Sigmar1-/- exacerbated ISO-induced gut microbiota dysbiosis, which was demonstrated by the lower abundance of probiotics g_Akkermansia and g_norank_f_Muribaculaceae, and higher abundance of pathogenic g_norank_f_Oscillospiraceae and Allobaculum. Furthermore, differential metabolites among WT-Control, WT-ISO and Sigmar-/--ISO groups were mainly enriched in bile secretion, tryptophan metabolism and phenylalanine metabolism, which presented a close association with microbial dysbiosis. Corresponding with the exacerbation of the microbiome, the inflammation-related NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, NF-kappa B signaling pathway and TNF signaling pathway were activated in the heart tissues.
Conclusion: Taken together, this study provides evidence that a Sigmar1 knockout disturbs the gut microbiota and remodels the serum metabolome, which may exacerbate HF by stimulating heart inflammation.
Keywords: gut microbiota; heart failure; inflammation; sigma-1 receptor; transcriptomics; untargeted metabolomics.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Zhang, Shen, Liu, Li, Chen, Liu, Li, Zhao, Wang and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bai Y., Shen Y., Xu X. Y., Bai Y., Fang Y., Zhang M., et al. (2018). Growth arrest and dna damage inducible 45-beta activates pro-inflammatory cytokines and phagocytosis in the grass carp (ctenopharyngodon idella) after aeromonas hydrophila infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 87, 176–181. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.06.010 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

