Synthetic 5-amino-6-D-ribitylaminouracil paired with inflammatory stimuli facilitates MAIT cell expansion in vivo
- PMID: 37720229
- PMCID: PMC10500299
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1109759
Synthetic 5-amino-6-D-ribitylaminouracil paired with inflammatory stimuli facilitates MAIT cell expansion in vivo
Abstract
Introduction: Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are a population of innate-like T cells, which mediate host immunity to microbial infection by recognizing metabolite antigens derived from microbial riboflavin synthesis presented by the MHC-I-related protein 1 (MR1). Namely, the potent MAIT cell antigens, 5-(2-oxopropylideneamino)-6-D-ribitylaminouracil (5-OP-RU) and 5-(2-oxoethylideneamino)-6-D-ribitylaminouracil (5-OE-RU), form via the condensation of the riboflavin precursor 5-amino-6-D-ribitylaminouracil (5-A-RU) with the reactive carbonyl species (RCS) methylglyoxal (MG) and glyoxal (G), respectively. Although MAIT cells are abundant in humans, they are rare in mice, and increasing their abundance using expansion protocols with antigen and adjuvant has been shown to facilitate their study in mouse models of infection and disease.
Methods: Here, we outline three methods to increase the abundance of MAIT cells in C57BL/6 mice using a combination of inflammatory stimuli, 5-A-RU and MG.
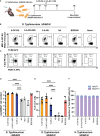
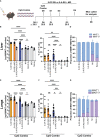
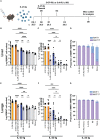
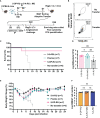
Results: Our data demonstrate that the administration of synthetic 5-A-RU in combination with one of three different inflammatory stimuli is sufficient to increase the frequency and absolute numbers of MAIT cells in C57BL/6 mice. The resultant boosted MAIT cells are functional and can provide protection against a lethal infection of Legionella longbeachae.
Conclusion: These results provide alternative methods for expanding MAIT cells with high doses of commercially available 5-A-RU (± MG) in the presence of various danger signals.
Keywords: 5-amino-6-D-ribitylaminouracil (5-A-RU); CpG; IL-23; MAIT cell boosting; MAIT cells; mouse model.
Copyright © 2023 Nelson, Wang, Dewar, Eddy, Li, Lim, Patton, Zhou, Pediongco, Meehan, Meehan, Mak, Fairlie, Stent, Kjer-Nielsen, McCluskey, Eckle, Corbett, Souter and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
JM, DF, LK-N, JMc, SE, AC, and ZC are inventors of patents WO2014/005194 and WO2015/149130 describing MR1 tetramers and MR1 ligands. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

