Navigating the challenges of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in lung cancer treatment: a propensity score study
- PMID: 37720497
- PMCID: PMC10503299
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359231198454
Navigating the challenges of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in lung cancer treatment: a propensity score study
Abstract
Background: Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) can negatively impact cancer patients' survival. It remains uncertain whether IPA's impact on patient outcomes varies by treatment approach in advanced lung cancer.
Objectives: To explore the association between IPA and outcomes in patients with advanced lung cancer receiving different treatments.
Design: A retrospective cohort study.
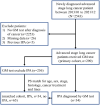
Methods: We enrolled patients with advanced-stage lung cancer between 2013 and 2021 at a college hospital in Taiwan and used the 2021 European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium consensus for IPA diagnosis. Multivariable logistic regression was used to identify the IPA risk factors. We compared overall survival (OS) and postgalactomannan (GM) test survival between the IPA and control groups using multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression and the Kaplan-Meier method with propensity score matching (PSM).
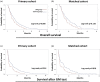
Results: Among 2543 patients with advanced-stage lung cancer, 290 underwent a GM test, of which 34 (11.7%) were diagnosed with IPA. Patients undergoing chemotherapy (HR = 4.02, p = 0.027) and immunotherapy [hazard ratio (HR) = 3.41, p = 0.076] tended to have IPA. Compared to the control group, the IPA group had shorter median OS (14.4 versus 9.9 months, p = 0.030) and post-GM test survival (4.5 versus 1.9 months, p = 0.003). IPA was associated with shorter OS (log-rank p = 0.014 and 0.018 before and after PSM, respectively) and shorter 1-year and 2-year survival post-GM test (HR = 1.65 and 1.66, respectively). Patients receiving chemotherapy or immunotherapy had a shorter post-GM test survival if they had IPA.
Conclusions: IPA tended to be diagnosed more frequently in patients receiving chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors. Patients diagnosed with IPA are associated with shorter survival. Larger cohort studies are needed to verify the observations.
Keywords: cancer survival; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; invasive pulmonary aspergillosis; lung cancer.
© The Author(s), 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Expression and differential diagnostic value of serum microRNA for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2017 Apr 12;40(4):272-277. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2017.04.006. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28395406 Chinese.
-
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: survival and prognostic factors.Haematologica. 2002 May;87(5):528-34. Haematologica. 2002. PMID: 12010668
-
[Galactomannan Tests of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid for Diagnosing Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Jan;49(1):124-128. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 29737102 Chinese.
-
[Diagnostic value of the combinations of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan test and serum galactomannan test in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Mar;31(3):331-335. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.03.014. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 30914095 Chinese.
-
Contribution of galactomannan antigen detection in BAL to the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies.Chest. 2010 Feb;137(2):410-5. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-0701. Epub 2009 Oct 3. Chest. 2010. PMID: 19801584
Cited by
-
Mapping the Burden of Fungal Diseases in the United Arab Emirates.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 May 15;10(5):353. doi: 10.3390/jof10050353. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786708 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and predictors of pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 28;12:1560288. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1560288. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40357295 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing and galactomannan testing for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31389. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82806-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kosmidis C, Denning DW. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax 2015; 70: 270–277. - PubMed
-
- Schauwvlieghe A, Rijnders BJA, Philips N, et al.. Invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe influenza: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med 2018; 6: 782–792. - PubMed
-
- Kuo CW, Wang SY, Tsai HP, et al.. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is associated with cytomegalovirus viremia in critically ill patients – a retrospective cohort study. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2022; 55: 291–299. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

