Primary ovarian insufficiency associated with lenvatinib therapy in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report
- PMID: 37720675
- PMCID: PMC10502945
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2023.14037
Primary ovarian insufficiency associated with lenvatinib therapy in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report
Abstract
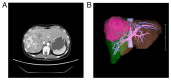
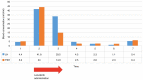
The therapeutic effects of molecular targeted drugs are, in some cases, more pronounced than those of conventional chemotherapy, and their introduction as a standard treatment is increasing. The present report describes a case of ovarian insufficiency in a young woman caused by tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib. The 25-year-old woman received lenvatinib (8 mg/day) for 98 days as preoperative chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Blood testing the day before starting lenvatinib administration indicated 4.40 mIU/ml luteinizing hormone (LH), 5.2 mIU/ml follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and age-equivalent hormone values. Amenorrhea occurred after the start of administration, and 48 days later, the LH level was 41.8 mIU/ml and the FSH level was 44 mIU/ml, indicating a decrease in ovarian function. The patient underwent hepatectomy, and 49 days after the end of lenvatinib administration, the LH level had improved to 4.5 mIU/ml and the FSH level had improved to 2.5 mIU/ml. After the hepatectomy, the patient began to have regular menstrual cycles once again. Ovarian toxicity has not been recognized as a side effect of lenvatinib. However, the present report describes primary ovarian insufficiency considered to be caused by this drug. Potential damage to ovarian function may need to be considered when molecular targeted drugs with the same mechanism of action as lenvatinib are used in young women.
Keywords: hepatocelluler carcinoma; lenvatinib; oncofertility; ovarian insufficiency; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright: © Aoki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of mifepristone (RU486) on the pituitary response to gonadotrophin releasing hormone in women.Hum Reprod. 1996 Dec;11(12):2585-90. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a019174. Hum Reprod. 1996. PMID: 9021355
-
Effects of Radioactive Iodine Therapy on Ovarian Reserve: A Prospective Pilot Study.Thyroid. 2018 Dec;28(12):1702-1707. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0129. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Thyroid. 2018. PMID: 30156472
-
Secondary amenorrhea and infertility caused by an inhibin-B-producing ovarian fibrothecoma.Fertil Steril. 2000 Feb;73(2):258-60. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(99)00511-7. Fertil Steril. 2000. PMID: 10685524
-
Effect of daily low dose mifepristone on the ovarian cycle and on dynamics of follicle growth.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1995 Oct;43(4):407-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1995.tb02610.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1995. PMID: 7586613 Clinical Trial.
-
Inhibin-producing ovarian granulosa cell tumor as a cause of secondary amenorrhea: case report and review of the literature.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2004 Dec;30(6):439-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2004.00231.x. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2004. PMID: 15566459 Review.
Cited by
-
Gonadotoxicity of immunotherapy and targeted agents in patients with cancer and impact on subsequent pregnancies.Hum Reprod. 2025 Aug 1;40(8):1452-1466. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaf096. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40482082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of clinical application of lenvatinib and its resistance mechanism in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):4113-4171. doi: 10.62347/UJVP4361. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
