Pharmacological Potential of Hippophae rhamnoides L. Nano-Emulsion for Management of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Animals' Model: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
- PMID: 37720770
- PMCID: PMC10500670
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04720
Pharmacological Potential of Hippophae rhamnoides L. Nano-Emulsion for Management of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Animals' Model: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
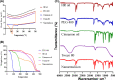
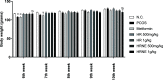
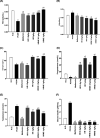
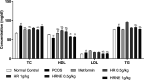
The most common female endocrinopathy, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), generally affects women of childbearing age. Hippophae rhamnoides L. has been traditionally used to improve menstrual cyclicity. Gas chromatography by flame ionization detection analysis showed that it contained various phytoconstituents such as omega-3 fatty acid, phytosterols, palmitic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid. H. rhamnoides L. (HR) nano-emulsion was also formulated. HR and its encapsulated nano-emulsion (HRNE) were evaluated for the treatment of PCOS. Thirty-five healthy female adult albino rats were acquired and divided into seven groups (n = 5). Letrozole (1 mg/kg) was used for 5 weeks to induce the disease. To confirm disease (PCOS) induction, the animals were weighed weekly and their vaginal smears were analyzed daily under a microscope. After PCOS induction, animals were treated with metformin, HR, and HRNE with two different doses (0.5/kg and 1 g/kg, p.o.) for 5 weeks. At the end of the treatment, animals were euthanized, and blood was collected for hormonal assessment, lipid profiling, and liver functioning test assessment. Both the ovaries were preserved for histopathology and liver for the purpose of assessment of antioxidant potential. The results revealed that HR and HRNE at both doses improved the hormonal imbalance; follicle-stimulating hormone, estrogen, and progesterone levels are increased, while luteinizing hormone surge and testosterone level are controlled. Insulin sensitivity is improved. Ovarian histopathology showed that normal ovarian echotexture is restored with corpus luteum and mature and developing follicles. HR and HRNE also improved the lipid profile and decreased lipid peroxidation (MDA) with improved antioxidant markers (SOD, CAT, and GSH). Results were statistically analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and were considered significant only if p < 0.05. In conclusion, it can be postulated that H. rhamnoides L. proved effective in the management of PCOS and its nano-emulsion effects were statistically more significant, which might be due to better bioavailability.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phytochemical-Based Study of Ethanolic Extract of Saraca asoca in Letrozole-Induced Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Female Adult Rats.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 1;8(45):42586-42597. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05274. eCollection 2023 Nov 14. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38024692 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals-based investigation of Rubia cordifolia pharmacological potential against letrozole-induced polycystic ovarian syndrome in female adult rats: In vitro, in vivo and mechanistic approach.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 9;10(14):e34298. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34298. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39108850 Free PMC article.
-
Dose Dependent Effects of Aqueous Extract of Garcinia cambogia Desr. Against Letrozole Induced Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Female Adult Rats With Possible Mechanisms Exploration.Dose Response. 2023 Apr 10;21(2):15593258231169381. doi: 10.1177/15593258231169381. eCollection 2023 Apr-Jun. Dose Response. 2023. PMID: 37063342 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Investigation of Standardized Aqueous Methanolic Extract of Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia L.) for Its Potential against Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Experimental Animals' Model: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Sep 29;2022:5143653. doi: 10.1155/2022/5143653. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36212951 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological changes in experimental polycystic ovary syndrome in female albino rats: Using either hemin or L-arginine.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8426-8435. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27757. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30443939 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical-Based Study of Ethanolic Extract of Saraca asoca in Letrozole-Induced Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Female Adult Rats.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 1;8(45):42586-42597. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05274. eCollection 2023 Nov 14. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38024692 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals-based investigation of Rubia cordifolia pharmacological potential against letrozole-induced polycystic ovarian syndrome in female adult rats: In vitro, in vivo and mechanistic approach.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 9;10(14):e34298. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34298. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39108850 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure using a cardiac targeting peptide linked to miRNA106a.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70432. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70432. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40820483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeng L.-H.; Rana S.; Hussain L.; Asif M.; Mehmood M. H.; Imran I.; Younas A.; Mahdy A.; Al-Joufi F. A.; Abed S. N. Polycystic ovary syndrome: a disorder of reproductive age, its pathogenesis, and a discussion on the emerging role of herbal remedies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 874914.10.3389/fphar.2022.874914T. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

