Synthesis and kinetic analysis of poly(N-acryloylmorpholine) brushes via surface initiated RAFT polymerization
- PMID: 37720872
- PMCID: PMC10504005
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0527.3528
Synthesis and kinetic analysis of poly(N-acryloylmorpholine) brushes via surface initiated RAFT polymerization
Abstract
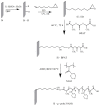
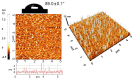
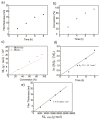
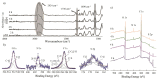
Polymer brushes are promising many applications as smart materials and biocompatible surfaces. Surface-initiated reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization is one of the most effective techniques for synthesis of well-defined polymer brushes. Herein, a biocompatible, uniform and stable poly(N-acryloylmorpholine)-silicon hybrid system was achieved using surface-initiated RAFT polymerization. Evidence of a well-controlled surface-initiated RAFT polymerization was confirmed by a linear increase of number average molecular weight (Mn) with overall monomer conversions. Water contact angle, ellipsometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy verified the presence of poly(N-acryloylmorpholine) (poly(NAM)) on silicon wafers. The grafting density (σ) and the average distance between grafting points (D) were estimated to be 0.58 chains/nm2 and 1.5 nm, respectively. The ratio of D value to radius of gyration (Rg) value is smaller than 1 (D/2Rg < 1), which corresponds to the brush regime of all grafted poly(NAM) films.
Keywords: Polymer brushes; poly(N-acryloyl morpholine); surface-initiated RAFT polymerization.
© TÜBİTAK.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Erratum: Preparation of Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) Functionalized SiO2 Beads for Protein Purification.J Vis Exp. 2019 Apr 30;(146). doi: 10.3791/6328. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31038480
-
RAFT-mediated synthesis of cationic poly[(ar-vinylbenzyl)trimethylammonium chloride] brushes for quantitative DNA immobilization.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013 Jan 1;33(1):111-20. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2012.08.015. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013. PMID: 25428051
-
Electrochemical deposition and surface-initiated RAFT polymerization: protein and cell-resistant PPEGMEMA polymer brushes.Biomacromolecules. 2010 Dec 13;11(12):3422-31. doi: 10.1021/bm1009365. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Biomacromolecules. 2010. PMID: 21028799
-
PNIPAM grafted surfaces through ATRP and RAFT polymerization: Chemistry and bioadhesion.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Mar 1;151:143-155. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.12.007. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017. PMID: 27992845 Review.
-
Mixed Polymer Brushes for "Smart" Surfaces.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jul 13;12(7):1553. doi: 10.3390/polym12071553. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32668820 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Micropatterning of Confined Surfaces with Polymer Brushes by Two-Photon-Initiated Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain-Transfer Polymerization.Small Sci. 2024 Nov 21;5(1):2400263. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400263. eCollection 2025 Jan. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40212642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai JT, Filla D, Shea R. Functional Polymers from Novel Carboxyl-Terminated Trithiocarbonates as Highly Efficient RAFT Agents. Macromolecules. 2002;35:6754–6756. doi: 10.1021/ma020362m. - DOI
-
- Bhayo AM, Yang Y, He X. Polymer brushes: Synthesis, characterization, properties and applications. Progress in Materials Science. 2022;130:101000–101040. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.101000. - DOI
-
- Chen WL, Cordero R, Tran H, Ober CK. 50th anniversary perspective: Polymer brushes: Novel surfaces for future materials. Macromolecules. 2017;50(11):4089–113. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b00450. - DOI
-
- Wang S, Wang Z, Li J, Li L, Hu W. Surface-grafting polymers: from chemistry to organic electronics. Materials Chemistry Frontiers. 2020;4:692–714. doi: 10.1039/C9QM00450E. - DOI
-
- Mocny P, Klok HA. Complex polymer topologies and polymer - nanoparticle hybrid films prepared via surface - initiated controlled radical polymerization. Progress in Polymer Science. 2020;100:101185–101202. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2019.101185. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
