Deep learning-based activity recognition and fine motor identification using 2D skeletons of cynomolgus monkeys
- PMID: 37721106
- PMCID: PMC10559098
- DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.449
Deep learning-based activity recognition and fine motor identification using 2D skeletons of cynomolgus monkeys
Abstract
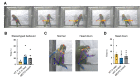
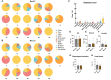
Video-based action recognition is becoming a vital tool in clinical research and neuroscientific study for disorder detection and prediction. However, action recognition currently used in non-human primate (NHP) research relies heavily on intense manual labor and lacks standardized assessment. In this work, we established two standard benchmark datasets of NHPs in the laboratory: MonkeyinLab (MiL), which includes 13 categories of actions and postures, and MiL2D, which includes sequences of two-dimensional (2D) skeleton features. Furthermore, based on recent methodological advances in deep learning and skeleton visualization, we introduced the MonkeyMonitorKit (MonKit) toolbox for automatic action recognition, posture estimation, and identification of fine motor activity in monkeys. Using the datasets and MonKit, we evaluated the daily behaviors of wild-type cynomolgus monkeys within their home cages and experimental environments and compared these observations with the behaviors exhibited by cynomolgus monkeys possessing mutations in the MECP2 gene as a disease model of Rett syndrome (RTT). MonKit was used to assess motor function, stereotyped behaviors, and depressive phenotypes, with the outcomes compared with human manual detection. MonKit established consistent criteria for identifying behavior in NHPs with high accuracy and efficiency, thus providing a novel and comprehensive tool for assessing phenotypic behavior in monkeys.
在神经科学及临床研究中,基于视频的动作识别方法日益成为神经疾病检测和预测的重要工具。然而,非人灵长类动物研究的动作识别目前仍依赖高强度的人工操作,并且缺乏标准化的评估方法,极大地影响研究效率及识别准确性。因此,该研究建立了在实验室环境下的两个非人灵长类动物基准数据集:MonkeyinLab (MiL) 数据集(包括13 类动作和姿态)和MiL2D数据集(包括15个2D 骨骼特征点),这两个标准数据集覆盖了食蟹猴的日常表型行为。此外,该研究还提出了一个基于深度学习的工具箱MonkeyMonitorKit (MonKit),MonKit采用TSSA网络识别猴子动作(准确度98.99%)和HRNet网络识别猴子的骨骼特征点(准确度98.8%),并结合动作姿势估计建立了精细动作的评估模型和行为分析方法,可评估疾病状态下的低头行为(抑郁症样表型)、刻板行为(自闭症样表型)等。该研究利用MonKit工具箱量化比较了作为 Rett 综合征疾病模型的MECP2 基因突变食蟹猴与野生型食蟹猴的日常行为分类和精细动作评估,并与人工识别进行对比,确认MonKit工具箱具备自动化、高效、标准统一、高准确率、高敏感性和低误差等优势,为非人灵长类的表型行为分类和评估提供了一种新颖而全面的研究手段。.
Keywords: 2D skeleton; Action recognition; Fine motor identification; Non-human primates; Rett syndrome.; Two-stream deep model.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modeling Rett Syndrome Using TALEN-Edited MECP2 Mutant Cynomolgus Monkeys.Cell. 2017 May 18;169(5):945-955.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.035. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28525759 Free PMC article.
-
Social-valence-related increased attention in rett syndrome cynomolgus monkeys: An eye-tracking study.Autism Res. 2019 Nov;12(11):1585-1597. doi: 10.1002/aur.2189. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Autism Res. 2019. PMID: 31389199
-
Autism-like behaviours and germline transmission in transgenic monkeys overexpressing MeCP2.Nature. 2016 Feb 4;530(7588):98-102. doi: 10.1038/nature16533. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26808898
-
Neuroanatomic and magnetic resonance imaging references for normal development of cerebral sulci of laboratory primate, cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2012 Mar;52(1):16-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-4520.2011.00352.x. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2012. PMID: 22348780 Review.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes in cynomolgus and rhesus monkeys and common marmosets in preclinical studies for humans.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;153:184-195. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.015. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29277691 Review.
Cited by
-
Study of tree shrew biology and models: A booming and prosperous field for biomedical research.Zool Res. 2024 Jul 18;45(4):877-909. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.199. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 39004865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BARN: Behavior-Aware Relation Network for multi-label behavior detection in socially housed macaques.Zool Res. 2023 Nov 18;44(6):1026-1038. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.485. Zool Res. 2023. PMID: 37804114 Free PMC article.
-
From beasts to bytes: Revolutionizing zoological research with artificial intelligence.Zool Res. 2023 Nov 18;44(6):1115-1131. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2023.263. Zool Res. 2023. PMID: 37933101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
InteBOMB: Integrating generic object tracking and segmentation with pose estimation for animal behavior analysis.Zool Res. 2025 Mar 18;46(2):355-369. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.268. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 40049663 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Attentiveness and Cognitive Engagement across Tasks using Video-based Action Understanding in Non-Human Primates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 3:2025.05.31.657183. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.31.657183. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501819 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Ahmad Z, Khan N Human action recognition using deep multilevel multimodal (M2) fusion of depth and inertial sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal. 2020;20(3):1445–1455. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2947446. - DOI
-
-
Andriluka M, Pishchulin L, Gehler P, et al. 2014. 2D human pose estimation: new benchmark and state of the art analysis. In: Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus: IEEE.
-
-
- Ben Mabrouk A, Zagrouba E Abnormal behavior recognition for intelligent video surveillance systems: a review. Expert Systems with Applications. 2018;91:480–491. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.09.029. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
