Polyoxidovanadates a new therapeutic alternative for neurodegenerative and aging diseases
- PMID: 37721286
- PMCID: PMC10581577
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.380877
Polyoxidovanadates a new therapeutic alternative for neurodegenerative and aging diseases
Abstract
Aging is a natural phenomenon characterized by a progressive decline in physiological integrity, leading to a deterioration of cognitive function and increasing the risk of suffering from chronic-degenerative diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, cancer, diabetes, and neurodegeneration. Aging is considered the major risk factor for Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease develops. Likewise, diabetes and insulin resistance constitute additional risk factors for developing neurodegenerative disorders. Currently, no treatment can effectively reverse these neurodegenerative pathologies. However, some antidiabetic drugs have opened the possibility of being used against neurodegenerative processes. In the previous framework, Vanadium species have demonstrated a notable antidiabetic effect. Our research group evaluated polyoxidovanadates such as decavanadate and metforminium-decavanadate with preventive and corrective activity on neurodegeneration in brain-specific areas from rats with metabolic syndrome. The results suggest that these polyoxidovanadates induce neuronal and cognitive restoration mechanisms. This review aims to describe the therapeutic potential of polyoxidovanadates as insulin-enhancer agents in the brain, constituting a therapeutic alternative for aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Vanadium species; antidiabetic; brain; cognition; diabetes; insulin; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
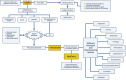
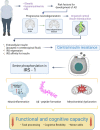

References
-
- Ahmadi-Eslamloo H, Dehghani GA, Moosavi SMS. Long-term treatment of diabetic rats with vanadyl sulfate or insulin attenuates acute focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via their antiglycemic effect. Metab Brain Dis. 2018;33:225–235. - PubMed
-
- Amante C, De Sousa-Coelho AL, Aureliano M. Vanadium and melanoma:a systematic review. Metals. 2021;11:828.
-
- Aureliano M, Ohlin CA. Decavanadate in vitro and in vivo effects:facts and opinions. J Inorg Biochem. 2014;137:123–130. - PubMed
-
- Aureliano M. The role of decavanadate in anti-tumor activity. Glob J Cancer Ther. 2017;3:12–14.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

