Activation of G-protein-coupled receptor 39 reduces neuropathic pain in a rat model
- PMID: 37721302
- PMCID: PMC10581569
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.380905
Activation of G-protein-coupled receptor 39 reduces neuropathic pain in a rat model
Abstract
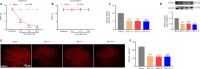
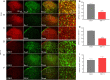
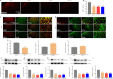
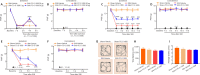
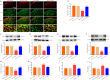
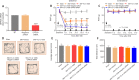
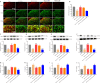
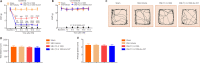
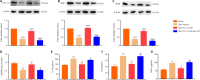
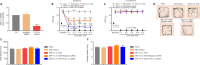
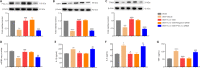
Activated G-protein-coupled receptor 39 (GPR39) has been shown to attenuate inflammation by interacting with sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α). However, whether GPR39 attenuates neuropathic pain remains unclear. In this study, we established a Sprague-Dawley rat model of spared nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain and found that GPR39 expression was significantly decreased in neurons and microglia in the spinal dorsal horn compared with sham-operated rats. Intrathecal injection of TC-G 1008, a specific agonist of GPR39, significantly alleviated mechanical allodynia in the rats with spared nerve injury, improved spinal cord mitochondrial biogenesis, and alleviated neuroinflammation. These changes were abolished by GPR39 small interfering RNA (siRNA), Ex-527 (SIRT1 inhibitor), and PGC-1α siRNA. Taken together, these findings show that GPR39 activation ameliorates mechanical allodynia by activating the SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway in rats with spared nerve injury.
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptor 39 (GPR39); mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM); neuroinflammation; neuropathic pain; nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1); peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γcoactivator 1α(PGC-1α); sirtuin 1 (SIRT1); spinal cord.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of GPR39 with TC-G 1008 attenuates neuroinflammation via SIRT1/PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway post-neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury in rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Oct 13;18(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02289-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34645465 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Protein 22 Attenuates Nerve Injury-induced Neuropathic Pain Via Improving Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Reducing Oxidative Stress Mediated By Spinal AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway in Male Rats.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 6;19(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10100-6. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38319409
-
β2-adrenoreceptor agonist ameliorates mechanical allodynia in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain via induction of mitochondrial biogenesis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Dec;144:112331. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112331. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34673421
-
Translocator Protein (TSPO) Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Activating Spinal Autophagy and Nuclear SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling in a Rat L5 SNL Model.J Pain Res. 2022 Mar 24;15:767-778. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S359397. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35356265 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mitochondria in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Influencing the NAD+-dependent SIRT1-PGC-1α-TFAM pathway.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;145:177-209. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31208524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GDF11 Mitigates Neuropathic Pain via Regulation of Microglial Polarization and Neuroinflammation through TGF-βR1/SMAD2/NF-κB Pathway in Male Mice.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 12;20(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10172-y. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39939465
-
MFG-E8 Ameliorates Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain by Regulating Microglial Polarization and Neuroinflammation via Integrin β3/SOCS3/STAT3 Pathway in Mice.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 21;19(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10150-w. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39305375
-
Sirtuin1 in Spinal Cord Injury: Regulatory Mechanisms, Microenvironment Remodeling and Therapeutic Potential.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Feb;31(2):e70244. doi: 10.1111/cns.70244. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 39915897 Free PMC article.
-
CTRP9 attenuates peripheral nerve injury-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia through regulating spinal microglial polarization and neuroinflammation mediated by AdipoR1 in male mice.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Oct 26;40(1):91. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09933-x. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39460844 Free PMC article.
-
Protein arginine methyltransferase-6 regulates heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-F expression and is a potential target for the treatment of neuropathic pain.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Sep 1;20(9):2682-2696. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01539. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39503430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bădescu L, Bădulescu O, Ciocoiu M, Bădescu M. Modulation of neuropathic pain in experimental diabetes mellitus. J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70:355–361. - PubMed
-
- Bordone L, Guarente L. Calorie restriction, SIRT1 and metabolism:understanding longevity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:298–305. - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira D, Lantéri-Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain. 2008;136:380–387. - PubMed
-
- Chai X, Zhang W, Chang B, Feng X, Song J, Li L, Yu C, Zhao J, Si H. GPR39 agonist TC-G 1008 promotes osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in MC3T3-E1 cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47:3569–3576. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

