Ultrasound improves the low-sodium salt curing of sea bass: Insights into the effects of ultrasound on texture, microstructure, and flavor characteristics
- PMID: 37722247
- PMCID: PMC10518730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106597
Ultrasound improves the low-sodium salt curing of sea bass: Insights into the effects of ultrasound on texture, microstructure, and flavor characteristics
Abstract
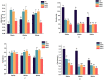
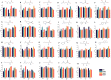
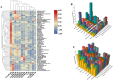
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of ultrasonic pretreatment on the quality of cured sea bass. Compared to static marination, ultrasonication significantly increased the rate of NaCl transfer, reduced the hardness and chewiness of fish, and improved water retention. Microstructural observations revealed that the sea bass muscle fibers were severely fragmented, with their borders becoming increasingly blurred with increasing ultrasonic intensity. In addition, ultrasound-assisted marination significantly increased the degradation of proteins, total free amino acid levels, and relative levels of volatile flavor substances such as aldehydes and esters. Therefore, the use of an appropriate ultrasound treatment for the salt curing of fish has a positive effect on the textural and flavor characteristics of sea bass, with the most optimal approach being 300.W ultrasound treatment for 60 min. Overall, the results of this study provide technical evidence for improving the quality of lightly cured low-salt content seafood.
Keywords: Flavor; Low-salt curing; Microstructure; Sea bass; Ultrasound-assisted curing.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Integration of untargeted lipidomics and targeted metabolomics revealed the mechanism of flavor formation in lightly cured sea bass driven via salt.Food Chem. 2025 Apr 1;470:142675. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.142675. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39756082
-
Effects of ultrasound-assisted low-salt curing on water retention, tenderness and in vitro digestive characteristics of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon Idellus).Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Feb;113:107214. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107214. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39754843 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of ultrasound-assisted tomato sour soup marination on beef: Insights into physicochemical, sensory, microstructural, and flavour characteristics.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Nov;110:107028. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107028. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 39167838 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-assisted low-sodium salt curing to modify the quality characteristics of beef for aging.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Dec;111:107134. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107134. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 39515261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel NaCl reduction technologies for dry-cured meat products and their mechanisms: A comprehensive review.Food Chem. 2024 Jan 15;431:137142. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137142. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 37591146 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Aloe vera Gel as a Natural Antioxidant on the Quality of Cold-Stored Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax).Foods. 2025 Mar 28;14(7):1185. doi: 10.3390/foods14071185. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238344 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Quality Enhancement of Frozen Tuna Fillets Using Ultrasound-Assisted Salting: Physicochemical Properties, Histology, and Proteomics.Foods. 2024 Feb 8;13(4):525. doi: 10.3390/foods13040525. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38397502 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-driven modulation of myofibrillar protein conformation promotes salt uptake and taste enhancement in marinated chicken breast.Food Chem X. 2025 Aug 5;29:102864. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102864. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40823132 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Assisted Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysis in Food Processing: Mechanism and Parameters.Foods. 2023 Nov 4;12(21):4027. doi: 10.3390/foods12214027. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37959146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Effects of Novel Food Processing Methods on Food Proteins: A Review.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 11;13(6):e70373. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70373. eCollection 2025 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40501502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiao H., Yu J., Song L., Hu M., Guo H., Xue Y., Xue C. Characterization of flesh firmness and ease of separation in the fermentation of sea bass in terms of protein structure, texture, and muscle tissue structural changes. Food Res. Int. 2022;162(10) - PubMed
-
- Swales J. Salt, blood pressure and health. Nutr. Bull. 2001;26(2):133–139.
-
- Fan H., Luo Y., Yin X., Bao Y., Feng L. Biogenic amine and quality changes in lightly salt- and sugar-salted black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) fillets stored at 4°C. Food Chem. 2014;159(18):20–28. - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Fang Y., Zhang J., Feng L., Lv Y., Luo Y. Changes in quality and microbial succession of lightly salted and sugar-salted blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) fillets stored at 4°C. J. Food Protect. 2018;81(8):1293–1303. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Q., Huang S., Du Y., Xiao J., Wang M., Wang X., Shi W., Zhao Y. Quality improvement of tilapia fillets by light salting during repeated freezing-thawing: Contribution of structural rearrangement and molecular interactions. Food Chem. 2023;406(11) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

