Phase 3 SELENE study: ibrutinib plus BR/R-CHOP in previously treated patients with follicular or marginal zone lymphoma
- PMID: 37722354
- PMCID: PMC10709678
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010298
Phase 3 SELENE study: ibrutinib plus BR/R-CHOP in previously treated patients with follicular or marginal zone lymphoma
Abstract
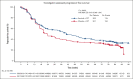
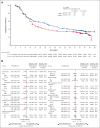
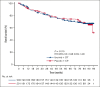
The phase 3 SELENE study evaluated ibrutinib + chemoimmunotherapy (CIT; bendamustine and rituximab [BR]; or rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone [R-CHOP]) for patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) follicular lymphoma (FL) or marginal zone lymphoma (MZL). Adult patients who had received ≥1 prior line of CIT were randomized 1:1 to oral ibrutinib (560 mg) or placebo daily, plus 6 cycles of BR/R-CHOP. The primary end point was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS). Overall, 403 patients were randomized to ibrutinib + CIT (n = 202) or placebo + CIT (n = 201). Most patients received BR (90.3%) and had FL (86.1%). With a median follow-up of 84 months, median PFS was 40.5 months in the ibrutinib + CIT arm and 23.8 months in the placebo + CIT arm (hazard ratio [HR], 0.806; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.626-1.037; P = .0922). Median overall survival was not reached in either arm (HR, 0.980; 95% CI, 0.686-1.400). Grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported in 85.6% and 75.4% of patients in the ibrutinib + CIT and placebo + CIT arms, respectively. In each arm, 13 patients had TEAEs leading to death. The addition of ibrutinib to CIT did not significantly improve PFS compared with placebo + CIT. The safety profile was consistent with known profiles of ibrutinib and CIT. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01974440.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: R.Q., M.C., T.H., M.R., M.T., and D.B.C. are employees of Janssen Research & Development and may own stock and options. H.N. has received honoraria from Janssen, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Celgene, Takeda, Eisai, Mundi Pharma, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Lilly, Meiji Seika Kaisha, AbbVie, GlaxoSmithKline, and Genmab, and is an employee of National Hospital Organization Nagoya Medical Center, which has received institutional research funding from Janssen, Celgene, AbbVie, Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ono Pharmaceutical, Zenyaku Kogyo, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Solasai Pharma, Kyowa Kirin, Nippon Shinyaku, Daiichi Sankyo, and Esai. P.M. has received advisory board honoraria from Roche, KITE, BeiGene, and Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene; speaker honoraria from Gilead, Takeda, and Janssen; and general honorarium from Incyte. W.M. has received grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Kywowa Krin, Genmab, Janssen, Nippon Shinyaku, and Ono Pharmaceutical, and speaker honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Nippon Shinyaku, Gilead Sciences, Eisai, Bristol Myers Squibb, SymBio, and Ono Pharmaceutical. M.Ö. has received research funding from AbbVie, Bayer, Janssen, Roche, Takeda, MSD, Pfizer, and Acerta, and travel expense reimbursement from AbbVie. L.J.N. has received advisory board honorarium and research support from Janssen. A.J. has received speaker honorarium from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, Incyte, Novartis, Sobi, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Takeda, and has served as a consultant on advisory boards for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, Incyte, Gilead, MSD, Novartis, Sobi, Sandoz, Sanofi-Genzyme, Roche, and Takeda. G.S. has received compensation for advisory board participation from AbbVie, Atbtherapeutics, Bayer, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Debiopharm, Epizyme, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Incyte, Ipsen, Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Loxo/Lilly, Molecular Partners, MorphoSys, Nordic Nanovector, Novartis, Regeneron, and Takeda, and is an Owkin shareholder. G.H. has received clinical research grants from Gilead/Kite, Incyte, Janssen, MorphoSys, Pfizer, Roche, and AbbVie; received consulting fees from AbbVie, ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genmab, Gilead/Kite, Incyte, Janssen, Miltenyi, Novartis, Roche, and Lilly; has received honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BieGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genmab, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, Roche, and Gilead/Kite; and has participated in data safety monitoring/advisory board for Miltenyi. I.D. has supported lectures for Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Eli Lilly, and Amgen, and has participated in clinical trials for AstraZeneca, MDS, and Novartis. F.M. has served as an advisory board consultant for Janssen, Gilead, MSD, Takeda, Roche, Novartis, and Incyte, and has received travel expense reimbursement from Takeda, Roche, Janssen, and Novartis. C.T. has supported conference work and advisory boards for Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Roche, Incyte, Kyte/Gilead, Amgen, and Takeda. M.A.P. has served on advisory boards for Janssen, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Merck, Ascentage Pharma, and Raffo; has served as a speaker for Janssen, AbbVie, and AstraZeneca; and has received travel grants from Roche, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and Raffo. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Ibrutinib in the treatment of relapsed FL and MZL?Blood Adv. 2023 Nov 28;7(22):7139-7140. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011400. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 38015493 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Monga N, Nastoupil L, Garside J, et al. Burden of illness of follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2019;98(1):175–183. - PubMed
-
- Ngu H, Takiar R, Phillips T, Okosun J, Sehn LH. Revising the treatment pathways in lymphoma: new standards of care – how do we choose? Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2022;42:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Chang C, Fraser CD, Zaidi O, Simon A, Bernauer M, Zhao Y. IBCL-425 disease burden and treatment patterns of relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma: a systematic literature review. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022;22(suppl 2):S391.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

