Aedes aegypti Argonaute 2 controls arbovirus infection and host mortality
- PMID: 37723154
- PMCID: PMC10507101
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41370-y
Aedes aegypti Argonaute 2 controls arbovirus infection and host mortality
Abstract
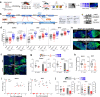
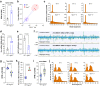
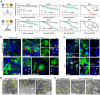
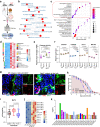
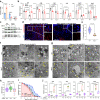
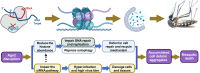
Ae. aegypti mosquitoes transmit some of the most important human viral diseases that are responsible for a significant public health burden worldwide. The small interfering RNA (siRNA) pathway is considered the major antiviral defense system in insects. Here we show that siRNA pathway disruption by CRISPR/Cas9-based Ago2 knockout impaired the mosquitoes' ability to degrade arbovirus RNA leading to hyper-infection accompanied by cell lysis and tissue damage. Ago2 disruption impaired DNA repair mechanisms and the autophagy pathway by altering histone abundance. This compromised DNA repair and removal of damaged cellular organelles and dysfunctional aggregates promoted mosquito death. We also report that hyper-infection of Ago2 knockout mosquitoes stimulated a broad-spectrum antiviral immunity, including apoptosis, which may counteract infection. Taken together, our studies reveal novel roles for Ago2 in protecting mosquitoes from arbovirus infection and associated death.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An Aedes aegypti-Derived Ago2 Knockout Cell Line to Investigate Arbovirus Infections.Viruses. 2021 Jun 3;13(6):1066. doi: 10.3390/v13061066. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34205194 Free PMC article.
-
The catalytic tetrad of Aedes aegypti argonaute 2 is critical for the antiviral activity of the exogenous siRNA pathway.J Biol Chem. 2025 Apr;301(4):108332. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108332. Epub 2025 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39984048 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral RNAi Response against the Insect-Specific Agua Salud Alphavirus.mSphere. 2022 Feb 23;7(1):e0100321. doi: 10.1128/msphere.01003-21. Epub 2022 Feb 16. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 35171691 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis for Arbovirus Transmission by Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes.Intervirology. 2018;61(6):255-264. doi: 10.1159/000499128. Epub 2019 May 13. Intervirology. 2018. PMID: 31082816 Review.
-
Deducing the Role of Virus Genome-Derived PIWI-Associated RNAs in the Mosquito-Arbovirus Arms Race.Front Genet. 2019 Nov 28;10:1114. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01114. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31850054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered antibody-mediated broad-spectrum suppression of human arboviruses in the Aedes aegypti vector.Commun Biol. 2025 May 7;8(1):709. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08133-5. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40335671 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout of the Corazonin Gene Indicates Its Regulation on the Cuticle Development of Desert Locusts (Schistocerca gregaria).Insects. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):704. doi: 10.3390/insects16070704. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40725333 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-flavivirus analysis reveals sfRNA-independent, 3' UTR-biased siRNA production from an insect-specific flavivirus.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0121524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01215-24. Epub 2024 Oct 15. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39404457 Free PMC article.
-
Wolbachia infection-responsive immune genes suppress Plasmodium falciparum infection in Anopheles stephensi.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Apr 10;20(4):e1012145. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012145. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38598552 Free PMC article.
-
Limited impact of the siRNA pathway on transposable element expression in Aedes aegypti.BMC Biol. 2025 May 13;23(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02225-8. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40361089 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

