Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Exacerbations in Hospitalized Patients From Admission to Discharge: A Comprehensive Review of Therapeutic Interventions
- PMID: 37724212
- PMCID: PMC10505355
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.43694
Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Exacerbations in Hospitalized Patients From Admission to Discharge: A Comprehensive Review of Therapeutic Interventions
Abstract
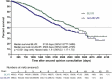
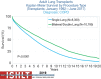
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common and debilitating condition that often necessitates hospitalization for exacerbations. Since COPD exacerbations can cause significant morbidity and mortality, managing them is crucial for patient care. Effective management of COPD exacerbations is essential to prevent complications, as COPD exacerbations are associated with increased healthcare costs and decreased quality of life. This review aims to comprehensively discuss the management of COPD exacerbations, covering various pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic strategies. These include inhaled bronchodilators, systemic steroids, antibiotics, invasive and non-invasive ventilation, oxygen therapy, smoking cessation, immunization with pneumococcal vaccine, inhalers at discharge, pulmonary rehabilitation, long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT), ambulatory oxygen therapy, short-burst oxygen therapy, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS), endobronchial procedures, and lung transplant. It is drawn upon various sources, including clinical studies, systemic reviews, and observational studies, to provide a comprehensive overview of current practices and identify areas for future research and innovation in managing COPD exacerbations. Addressing these areas of interest can improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(copd); clinical outcomes; copd exacerbation; copd: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; invasive ventilation; non invasive ventilation; therapeutic interventions.
Copyright © 2023, Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Acute exacerbation of COPD: clinical perspectives and literature review. Erhabor GE, Adeniyi B, Arawomo AO, et al. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34922414/ West Afr J Med. 2021;Vol. 38:1129–1142. - PubMed
-
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Lareau SC, Fahy B, Meek P, Wang A. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;199:0–2. - PubMed
-
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [ Mar; 2023 ]. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pul... https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pul...
-
- Agarwal AK, Raja A, Brown BD. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls [Internet], StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
