Understanding recurrent pregnancy loss: recent advances on its etiology, clinical diagnosis, and management
- PMID: 37724255
- PMCID: PMC10471095
- DOI: 10.1515/mr-2022-0030
Understanding recurrent pregnancy loss: recent advances on its etiology, clinical diagnosis, and management
Abstract
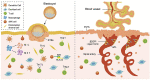
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) has become an important reproductive health issue worldwide. RPL affects about 2%-3% of reproductive-aged women, and makes serious threats to women's physical and mental health. However, the etiology of approximately 50% of RPL cases remains unknown (unexplained RPL), which poses a big challenge for clinical management of these patients. RPL has been widely regarded as a complex disease where its etiology has been attributed to numerous factors. Heretofore, various risk factors for RPL have been identified, such as maternal ages, genetic factors, anatomical structural abnormalities, endocrine dysfunction, prethrombotic state, immunological factors, and infection. More importantly, development and applications of next generation sequencing technology have significantly expanded opportunities to discover chromosomal aberrations and single gene variants responsible for RPL, which provides new insight into its pathogenic mechanisms. Furthermore, based upon patients' diagnostic evaluation and etiologic diagnosis, specific therapeutic recommendations have been established. This review will highlight current understanding and recent advances on RPL, with a special focus on the immunological and genetic etiologies, clinical diagnosis and therapeutic management.
Keywords: etiologic diagnosis; genetic etiology; next generation sequencing; recurrent pregnancy loss; therapeutic recommendations.
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Obstetrics subgroup, Chinese society of Obstetrics and Gynecology; Chinese medical association; Chinese expert consensus group on diagnosis and management of recurrent spontaneous abortion. Chinese expert consensus on diagnosis and management of recurrent spontaneous abortion (2022) Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2022;57:653–67. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
