Leptin signaling and leptin resistance
- PMID: 37724323
- PMCID: PMC10388810
- DOI: 10.1515/mr-2022-0017
Leptin signaling and leptin resistance
Abstract
With the prevalence of obesity and associated comorbidities, studies aimed at revealing mechanisms that regulate energy homeostasis have gained increasing interest. In 1994, the cloning of leptin was a milestone in metabolic research. As an adipocytokine, leptin governs food intake and energy homeostasis through leptin receptors (LepR) in the brain. The failure of increased leptin levels to suppress feeding and elevate energy expenditure is referred to as leptin resistance, which encompasses complex pathophysiological processes. Within the brain, LepR-expressing neurons are distributed in hypothalamus and other brain areas, and each population of the LepR-expressing neurons may mediate particular aspects of leptin effects. In LepR-expressing neurons, the binding of leptin to LepR initiates multiple signaling cascades including janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-protein kinase B (AKT), extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK), and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling, etc., mediating leptin actions. These findings place leptin at the intersection of metabolic and neuroendocrine regulations, and render leptin a key target for treating obesity and associated comorbidities. This review highlights the main discoveries that shaped the field of leptin for better understanding of the mechanism governing metabolic homeostasis, and guides the development of safe and effective interventions to treat obesity and associated diseases.
Keywords: leptin; leptin cellular pathways; leptin neural pathways; leptin resistance.
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
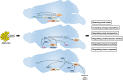
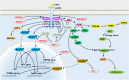
 : Activating;
: Activating;  : Inhibiting;
: Inhibiting;  : Translocation. ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AgRP, agouti-related peptide; AKT, protein kinase B; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; ATP, adenosine-5′-triphosphate; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; FoxO1, forkhead box protein O1; HDAC5, histone deacetylases 5; HSP60, heat shock protein: 60; IRS, insuline receptor substrate; JAK2, janus kinases 2; LCFA-CoA, long chain fatty acid-coenzyme A; LepR, leptin receptor; MAGEL2, melanoma antigen-like gene 2; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NPY, neuropeptide Y; PDE3B, phosphodiesterase 3B; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; POMC, proopiomelanocortin; PTP1B, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; ROCK1, Rho-kinasel; S6K, S6 kinase; SF1, steroidogenic factor 1; SH2B1, Src-homology-2 B adaptor protein-1; SHP2, SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2; SIRT1, NAD+-dependent deacetylase sirtuin 1; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; TCPTP, T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase.
: Translocation. ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AgRP, agouti-related peptide; AKT, protein kinase B; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; ATP, adenosine-5′-triphosphate; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; FoxO1, forkhead box protein O1; HDAC5, histone deacetylases 5; HSP60, heat shock protein: 60; IRS, insuline receptor substrate; JAK2, janus kinases 2; LCFA-CoA, long chain fatty acid-coenzyme A; LepR, leptin receptor; MAGEL2, melanoma antigen-like gene 2; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NPY, neuropeptide Y; PDE3B, phosphodiesterase 3B; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate; POMC, proopiomelanocortin; PTP1B, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; ROCK1, Rho-kinasel; S6K, S6 kinase; SF1, steroidogenic factor 1; SH2B1, Src-homology-2 B adaptor protein-1; SHP2, SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2; SIRT1, NAD+-dependent deacetylase sirtuin 1; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; TCPTP, T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase.Similar articles
-
Leptin signalling pathways in hypothalamic neurons.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Apr;73(7):1457-77. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2133-1. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26786898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRS2 signaling in LepR-b neurons suppresses FoxO1 to control energy balance independently of leptin action.Cell Metab. 2012 May 2;15(5):703-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.011. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22560222 Free PMC article.
-
Altered function of arcuate leptin receptor expressing neuropeptide Y neurons depending on energy balance.Mol Metab. 2023 Oct;76:101790. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101790. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Mol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37562743 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin signaling in the hypothalamus: emphasis on energy homeostasis and leptin resistance.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2003 Dec;24(4):225-53. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2003.10.001. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2003. PMID: 14726256 Review.
-
Unsilencing of native LepRs in hypothalamic SF1 neurons does not rescue obese phenotype in LepR-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019 Sep 1;317(3):R451-R460. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00111.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31314542
Cited by
-
Role of Leptin in Obesity, Cardiovascular Disease, and Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 16;25(4):2338. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042338. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E-Cigarette Exposure Alters Neuroinflammation Gene and Protein Expression in a Murine Model: Insights from Perinatally Exposed Offspring and Post-Birth Mothers.Genes (Basel). 2024 Mar 1;15(3):322. doi: 10.3390/genes15030322. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540381 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of modulating leptin sensitivity on the transcriptomic profile of adult-derived hypothalamic mouse neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jan 17;17:1518737. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1518737. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39916981 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Imprints of Clinical Comorbidities in Hypothalamic Extracellular Vesicles at the Onset of Obesity.ACS Omega. 2025 May 29;10(22):23563-23581. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02274. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40521556 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary insight into the potential role of Leptin Receptor Polymorphisms in Type 2 Diabetes Risk: case-control study and bioinformatics analysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 May 3;24(1):113. doi: 10.1007/s40200-025-01617-5. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40331155
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
