Long follow-up of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in healthcare workers (2020-2022): A retrospective longitudinal SARS-CoV-2 serological surveillance
- PMID: 37724517
- PMCID: PMC10512804
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2258632
Long follow-up of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in healthcare workers (2020-2022): A retrospective longitudinal SARS-CoV-2 serological surveillance
Abstract
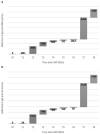
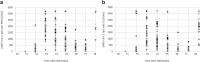
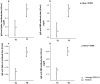
SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike IgG production and protection from severe respiratory illness should be explored in greater depth after COVID-19 booster vaccination. This longitudinal observational retrospective study investigated the anti-spike IgG response elicited by the first, second and booster doses of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in healthcare workers (HCW) at San Martino IRCCS Policlinico Hospital (Genoa) up to the 12th month. Sequential blood sampling was performed at T0 (prior to vaccination), T1 (21 days after the 1st dose of vaccine), T2, T3, T4, T5, T6 (7 days and 1, 3, 6 and 9 months after the 2nd dose, respectively), T7 and T8 (1 and 3 months after a booster dose). A SARS-CoV-2 IgG panel (Bio-Rad, Marnes-la-Coquette, France) was used to determine levels of receptor-binding domain (RBD), spike-1 (S1), spike-2 and nucleocapsid structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2. In the 51 HCWs evaluated, seroprevalence was 96% (49/51) at T1 and 100% (51/51) from T2 to T5 for RBD and S1. At T6, only one HCW was negative. T2 [RBD = 2945 (IQR:1693-5364); S1 = 1574 (IQR:833-3256) U/mL], and T7 [RBD = 8204 (IQR:4129-11,912); S1 = 4124 (IQR:2124-6326) U/mL] were characterized by the highest antibody values. Significant humoral increases in RBD and S1 were documented at T7 and T8 compared to T2 and T4, respectively (p-value < .001). Following vaccination with BNT162b2 and a booster dose in the 9th month, naïve and healthy subjects show high antibody titers up to 12 months and a protective humoral response against COVID-19 disease lasting up to 20 months after the last booster.
Keywords: BNT162b2 vaccine; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; anti-spike IgG seroprevalence; healthcare workers.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. [accessed 2023 Aug 7]. https://covid19.who.int/.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . COVID-19. [accessed 2023 Aug 7]. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/index.html.
-
- Frenck RW Jr, Klein NP, Kitchin N, Gurtman A, Absalon J, Lockhart S, Perez JL, Walter EB, Senders S, Bailey R, et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 covid-19 vaccine in adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(3):239–50. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107456. PMID: 34043894. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
