Clinical Evaluation of a Novel Combination of Sodium Hypochlorite/Amino Acid and Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid Adjunctive to Non-surgical Periodontal Treatment: A Case Series
- PMID: 37724897
- PMCID: PMC11619905
- DOI: 10.3290/j.ohpd.b4347453
Clinical Evaluation of a Novel Combination of Sodium Hypochlorite/Amino Acid and Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid Adjunctive to Non-surgical Periodontal Treatment: A Case Series
Abstract
Purpose: The adjunctive subgingival application of sodium hypochlorite/amino acid and a mixture of natural and cross-linked hyaluronic acid gels (high molecular weight) has been recently proposed as a novel modality to enhance the outcomes of non-surgical periodontal therapy. The aim of this prospective case series was to evaluate the clinical outcomes obtained following the subgingival application of a combination of sodium hypochlorite/amino acid and a mixture of natural and cross-linked hyaluronic acid (high molecular) gels in conjunction with non-surgical periodontal therapy.
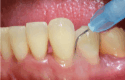
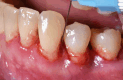
Material and methods: Twenty-one systemically healthy, non-smoking patients diagnosed with stage II-III, grade A/B periodontitis underwent full-mouth subgingival debridement (SD) performed with ultrasonic and hand instruments. All sites with probing depths (PD) ≥ 4 mm were treated with additional repeated (i.e., 2-3 times) instillation of sodium hypochlorite/amino acid gel in the periodontal pockets prior to and during SRP. Following mechanical debridement, a mixture of natural and cross-linked hyaluronic acid (high molecular) gel was applied in the pockets. The primary outcome variable was PD reduction; changes in clinical attachment level (CAL) and bleeding on probing (BOP) were the secondary outcomes. The clinical parameters were assessed at baseline, 3 and 6 months after therapy.
Results: Compared to baseline, a statistically significant mean reduction of PD values was obtained after 3 and 6 months, amounting to 2.6 ± 0.4 mm, and 2.9 ± 0.4 mm, respectively (p < 0.001). Mean CAL gain measured 2.3 ± 0.5 mm at 3 months and 2.6 ± 0.5 mm at 6 months in comparison to baseline (p < 0.001). Mean reduction of BOP values was 54.9 ± 16.9 % at 3 months and 65.6 ± 16.4 % at 6 months (p < 0.001). The number of moderate pockets (4-5 mm) decreased from 1808 at baseline to 274 at the 6-month evaluation, and the number of deep (≥ 6 mm) pockets dropped from 319 to 3, respectively.
Conclusion: The combination of sodium hypochlorite/amino acid and a mixture of natural and cross-linked hyaluronic acid (high molecular) adjunctive to subgingival debridement may represent a valuable approach to improve the outcomes of non-surgical periodontal treatment.
Keywords: cross-linked hyaluronic acid; non-surgical periodontal therapy; periodontitis; sodium hypochlorite/amino acid..
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical evaluation of sodium hypochlorite/amino acids and cross-linked hyaluronic acid adjunctive to non-surgical periodontal treatment: a randomized controlled clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Nov;27(11):6645-6656. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05271-0. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 37740107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Non-surgical treatment of residual periodontal pockets using sodium hypochlorite/amino acid gel and cross-linked hyaluronic acid-a 9-month pilot randomized controlled clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Sep 5;28(9):513. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05906-w. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 39235513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in clinical parameters following adjunctive local sodium hypochlorite gel in minimally invasive nonsurgical therapy (MINST) of periodontal pockets: a 6-month randomized controlled clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2021 Sep;25(9):5331-5340. doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-03841-8. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Clin Oral Investig. 2021. PMID: 33687555 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sodium Hypochlorite as an Adjunct to Nonsurgical Treatment of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020 Oct 13;18(4):881-887. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a45405. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020. PMID: 33215480 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid as adjunctive to non-surgical and surgical periodontal therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2019 Sep;23(9):3423-3435. doi: 10.1007/s00784-019-03012-w. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Clin Oral Investig. 2019. PMID: 31338632
Cited by
-
Non-Surgical Treatment of Moderate Periodontal Intrabony Defects With Adjunctive Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid: A Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.J Clin Periodontol. 2025 Feb;52(2):310-322. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.14078. Epub 2024 Oct 14. J Clin Periodontol. 2025. PMID: 39402910 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Histological evaluation of nonsurgical periodontal treatment with and without the use of sodium hypochlorite / amino acids and cross-linked hyaluronic acid gels in dogs.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Apr 27;28(5):281. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05674-7. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38676852 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiological Effects of Sodium Hypochlorite/-Amino Acids and Cross-linked Hyaluronic Acid Adjunctive to Non-surgical Periodontal Treatment.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2024 Apr 30;22:171-180. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.b5281925. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2024. PMID: 38687029 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical evaluation of sodium hypochlorite/amino acids and cross-linked hyaluronic acid adjunctive to non-surgical periodontal treatment: a randomized controlled clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Nov;27(11):6645-6656. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05271-0. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 37740107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Non-surgical treatment of residual periodontal pockets using sodium hypochlorite/amino acid gel and cross-linked hyaluronic acid-a 9-month pilot randomized controlled clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Sep 5;28(9):513. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05906-w. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 39235513 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Belibasakis GN, Belstrøm D, Eick S, Gursoy UK, Johansson A, Könönen E. Periodontal microbiology and microbial etiology of periodontal diseases: Historical concepts and contemporary perspectives. Periodontol 2000. 2023 (20 Jan) 10.1111/prd.12473. - PubMed
-
- Costa FO, Takenaka-Martinez S, Cota LOM, Ferreira SD, Silva GLM, Costa JE. Peri-implant disease in subjects with and without preventive maintenance: a 5-year follow-up. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(2):173–181. - PubMed
-
- Darveau RP, Curtis MA. Oral biofilms revisited: A novel host tissue of bacteriological origin. Periodontol 2000. 2021;86(1):8–13. - PubMed
-
- de Brito Bezerra B, Mendes Brazão MA, de Campos MLG, Casati MZ, Sallum EA, Sallum AW. Association of hyaluronic acid with a collagen scaffold may improve bone healing in critical-size bone defects. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(8):938–942. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical