A Predictive Model for the Early Death of Breast Cancer With Synchronous Liver Metastases: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 37724916
- PMCID: PMC10510350
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748231202851
A Predictive Model for the Early Death of Breast Cancer With Synchronous Liver Metastases: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer liver metastasis (BCLM) is a severe condition often resulting in early death. The identification of prognostic factors and the construction of accurate predictive models can guide clinical decision-making.
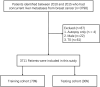
Methods: A large sample of data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database was analyzed, including 3711 patients diagnosed with de novo BCLM between 2010 and 2015. Predictive models were developed using histograms, and stepwise regression addressed variable collinearity. Internal validation was performed, and results were compared to similar studies.
Results: In this study of 3711 BCLM patients, 2571 didn't have early death. Out of the 1164 who died early, 1086 had cancer-specific early death. Prognostic factors for early death, including age, race, tumor size, and lymph node involvement, were identified. A nomogram based on these factors was constructed, accurately predicting early all-cause and cancer-specific death.
Conclusions: Valuable insights into the prognosis of BCLM patients were provided, and important prognostic factors for early death were identified. The developed nomogram can assist clinicians in identifying high-risk patients for early death and inform treatment decisions.
Keywords: End Results; Surveillance, Epidemiology, and; breast cancer; liver metastases; nomogram; prognostic model.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Early death prediction model for breast cancer with synchronous lung metastases: an analysis of the SEER database.Gland Surg. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):1708-1728. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-240. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39544977 Free PMC article.
-
An effective tool for predicting survival in breast cancer patients with de novo lung metastasis: Nomograms constructed based on SEER.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 6;9:939132. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.939132. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684376 Free PMC article.
-
Risk and prognostic factors of breast cancer with liver metastases.BMC Cancer. 2021 Mar 6;21(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07968-5. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33676449 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor conversion and survival in breast cancer liver metastases.Breast Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 13;25(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01706-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37705026 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the metastatic mechanism and progress in the treatment of breast cancer liver metastasis: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 30;12(6):1635-1646. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-2463. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37434684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Real-time survival assessment in breast cancer with liver metastasis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 23;16(1):1184. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02999-x. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40549258 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronous multiple primary cancers involving cervical cancer and follicular lymphoma: A case report.Oncol Lett. 2025 Feb 13;29(4):183. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14930. eCollection 2025 Apr. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40007622 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

