A hypernetwork-based urn model for explaining collective dynamics
- PMID: 37725633
- PMCID: PMC10508602
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291778
A hypernetwork-based urn model for explaining collective dynamics
Abstract
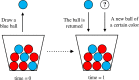
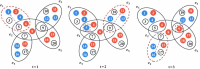
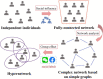
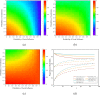
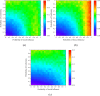
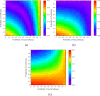
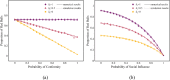
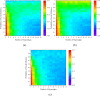
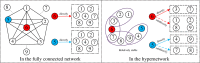
The topological characterization of complex systems has significantly contributed to our understanding of the principles of collective dynamics. However, the representation of general complex networks is not enough for explaining certain problems, such as collective actions. Considering the effectiveness of hypernetworks on modeling real-world complex networks, in this paper, we proposed a hypernetwork-based Pólya urn model that considers the effect of group identity. The mathematical deduction and simulation experiments show that social influence provides a strong imitation environment for individuals, which can prevent the dynamics from being self-correcting. Additionally, the unpredictability of the social system increases with growing social influence, and the effect of group identity can moderate market inequality caused by individual preference and social influence. The present work provides a modeling basis for a better understanding of the logic of collective dynamics.
Copyright: © 2023 Lu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research on mechanisms for optimizing the risk resistance capability of hypernetworks.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82394-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732751 Free PMC article.
-
A topic dissemination model based on hypernetwork.Sci Rep. 2025 May 15;15(1):16881. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01497-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40374777 Free PMC article.
-
Studying language change using price equation and Pólya-urn dynamics.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033171. Epub 2012 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22427981 Free PMC article.
-
Topological portraits of multiscale coordination dynamics.J Neurosci Methods. 2020 Jun 1;339:108672. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108672. Epub 2020 Mar 6. J Neurosci Methods. 2020. PMID: 32151601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural, psychological, and social foundations of collective memory: Implications for common mnemonic processes, agency, and identity.Prog Brain Res. 2022;274(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2022.07.004. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Prog Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 36167445 Review.
References
-
- Dholakia UM, Bagozzi RP, Pearo LK. A social influence model of consumer participation in network-and small-group-based virtual communities. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2004; 21: 241–263. 10.1016/j.ijresmar.2003.12.004 - DOI
-
- Chen W, Wang Y, Yang S. Efficient influence maximization in social networks. 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD). 2009; pp. 199–208. 10.1145/1557019.1557047 - DOI
-
- Ye M, Liu X, Lee WC. Exploring social influence for recommendation: a generative model approach. 35th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR). 2012; pp. 671–680. 10.1145/2348283.2348373 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

