Halide Perovskites and Their Derivatives for Efficient, High-Resolution Direct Radiation Detection: Design Strategies and Applications
- PMID: 37726105
- PMCID: PMC11475525
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202304523
Halide Perovskites and Their Derivatives for Efficient, High-Resolution Direct Radiation Detection: Design Strategies and Applications
Abstract
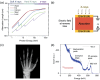
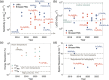
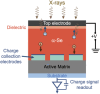
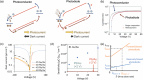
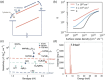
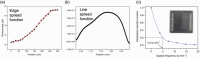
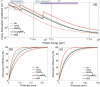
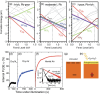
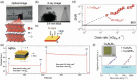
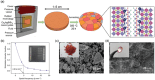
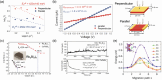
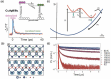
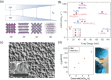
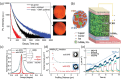
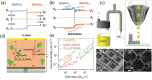
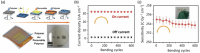
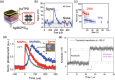
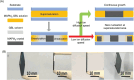
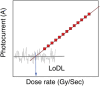
The past decade has witnessed a rapid rise in the performance of optoelectronic devices based on lead-halide perovskites (LHPs). The large mobility-lifetime products and defect tolerance of these materials, essential for optoelectronics, also make them well-suited for radiation detectors, especially given the heavy elements present, which is essential for strong X-ray and γ-ray attenuation. Over the past decade, LHP thick films, wafers, and single crystals have given rise to direct radiation detectors that have outperformed incumbent technologies in terms of sensitivity (reported values up to 3.5 × 106 µC Gyair -1 cm-2 ), limit of detection (directly measured values down to 1.5 nGyair s-1 ), along with competitive energy and imaging resolution at room temperature. At the same time, lead-free perovskite-inspired materials (e.g., methylammonium bismuth iodide), which have underperformed in solar cells, have recently matched and, in some areas (e.g., in polarization stability), surpassed the performance of LHP detectors. These advances open up opportunities to achieve devices for safer medical imaging, as well as more effective non-invasive analysis for security, nuclear safety, or product inspection applications. Herein, the principles behind the rapid rises in performance of LHP and perovskite-inspired material detectors, and how their properties and performance link with critical applications in non-invasive diagnostics are discussed. The key strategies to engineer the performance of these materials, and the important challenges to overcome to commercialize these new technologies are also discussed.
Keywords: charge-carrier kinetics; halide perovskites; imaging; ion migration; perovskite-inspired materials; radiation detectors; stability.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Materials published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kojima A., Teshima K., Shirai Y., Miyasaka T., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050. - PubMed
-
- Best Research‐Cell Efficiency Chart‐NREL, https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell‐efficiency.html (accessed: April 2023).
-
- Tan Z. K., Moghaddam R. S., Lai M. L., Docampo P., Higler R., Deschler F., Price M., Sadhanala A., Pazos L. M., Credgington D., Hanusch F., Bein T., Snaith H. J., Friend R. H., Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 687. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z., Qiu W., Peng X., Sun G., Liu X., Liu D., Li Z., He F., Shen C., Gu Q., Ma F., Yip H. L., Hou L., Qi Z., Su S. J., Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103268. - PubMed
-
- Min H., Lee D. Y., Kim J., Kim G., Lee K. S., Kim J., Paik M. J., Kim Y. K., Kim K. S., Kim M. G., Shin T. J., Il Seok S., Nature 2021, 598, 444. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

