Uncertainty analysis of contagion processes based on a functional approach
- PMID: 37726315
- PMCID: PMC10509249
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-42041-0
Uncertainty analysis of contagion processes based on a functional approach
Abstract
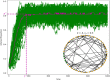
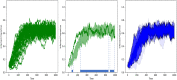
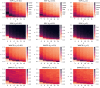
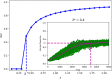
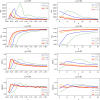
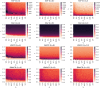
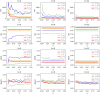
The spread of a disease, product or idea in a population is often hard to predict. We tend to observe one or few realizations of the contagion process and therefore limited information can be obtained for anticipating future similar events. The stochastic nature of contagion generates unpredictable outcomes throughout the whole course of the dynamics. This might lead to important inaccuracies in the predictions and to the over or under-reaction of policymakers, who tend to anticipate the average behavior. Through an extensive simulation study, we analyze properties of the contagion process, focusing on its unpredictability or uncertainty, and exploiting the functional nature of the data. In particular, we define a novel non-parametric measure of variance based on weighted depth-based central regions. We apply this methodology to the susceptible-infected-susceptible epidemiological model and small-world networks. We find that maximum uncertainty is attained at the epidemic threshold. The density of the network and the contagiousness of the process have a strong and complementary effect on the uncertainty of contagion, whereas only a mild effect of the network's randomness structure is observed.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Watts DJ, Yariv L. The “new” science of networks. Ann. Rev. Sociol. 2004;30:243–270. doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.30.020404.104342. - DOI
-
- Vega-Redondo, F. Complex Social Networks. Econometric Society Monographs (Cambridge University Press, 2007).
-
- Jackson MO, Yariv L. Diffusion of behavior and equilibrium properties in network games. Am. Econ. Rev. 2007;97:92–98. doi: 10.1257/aer.97.2.92. - DOI
-
- Pastor-Satorras R, Castellano C, Van Mieghem P, Vespignani A. Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Modern Phys. 2015;87:925–979. doi: 10.1103/revmodphys.87.925. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

