Myeloid-derived growth factor suppresses VSMC dedifferentiation and attenuates postinjury neointimal formation in rats by activating S1PR2 and its downstream signaling
- PMID: 37726422
- PMCID: PMC10770085
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-023-01155-x
Myeloid-derived growth factor suppresses VSMC dedifferentiation and attenuates postinjury neointimal formation in rats by activating S1PR2 and its downstream signaling
Abstract
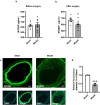
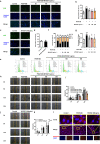
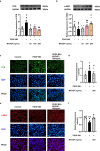
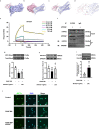
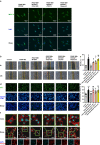
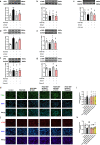
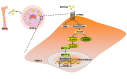
Restenosis after angioplasty is caused usually by neointima formation characterized by aberrant vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) dedifferentiation. Myeloid-derived growth factor (MYDGF), secreted from bone marrow-derived monocytes and macrophages, has been found to have cardioprotective effects. In this study we investigated the effect of MYDGF to postinjury neointimal formation and the underlying mechanisms. Rat carotid arteries balloon-injured model was established. We found that plasma MYDGF content and the level of MYDGF in injured arteries were significantly decreased after balloon injury. Local application of exogenous MYDGF (50 μg/mL) around the injured vessel during balloon injury markedly ameliorated the development of neointimal formation evidenced by relieving the narrow endovascular diameter, improving hemodynamics, and reducing collagen deposition. In addition, local application of MYDGF inhibited VSMC dedifferentiation, which was proved by reversing the elevated levels of osteopontin (OPN) protein and decreased levels of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in the left carotid arteries. We showed that PDGF-BB (30 ng/mL) stimulated VSMC proliferation, migration and dedifferentiation in vitro; pretreatment with MYDGF (50-200 ng/mL) concentration-dependently eliminated PDGF-BB-induced cell proliferation, migration and dedifferentiation. Molecular docking revealed that MYDGF had the potential to bind with sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2), which was confirmed by SPR assay and Co-IP analysis. Pretreatment with CCG-1423 (Rho signaling inhibitor), JTE-013 (S1PR2 antagonist) or Ripasudil (ROCK inhibitor) circumvented the inhibitory effects of MYDGF on VSMC phenotypic switching through inhibiting S1PR2 or its downstream RhoA-actin monomers (G-actin) /actin filaments (F-actin)-MRTF-A signaling. In summary, this study proves that MYDGF relieves neointimal formation of carotid arteries in response to balloon injury in rats, and suppresses VSMC dedifferentiation induced by PDGF-BB via S1PR2-RhoA-G/F-actin-MRTF-A signaling pathway. In addition, our results provide evidence for cross talk between bone marrow and vasculature.
Keywords: MYDGF, Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2; VSMC dedifferentiation; balloon injury; carotid artery; neointimal formation.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kanglexin counters vascular smooth muscle cell dedifferentiation and associated arteriosclerosis through inhibiting PDGFR.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul 25;130:155704. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155704. Epub 2024 May 1. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38759316
-
RhoGDI3 at the trans-Golgi network participates in NLRP3 inflammasome activation, VSMC phenotypic modulation, and neointima formation.Atherosclerosis. 2023 Dec;387:117391. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.117391. Epub 2023 Nov 19. Atherosclerosis. 2023. PMID: 38029612
-
Intermedin reduces neointima formation by regulating vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype via cAMP/PKA pathway.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Nov;266:212-222. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.10.011. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 29053988
-
Thymoquinone suppresses platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration and neointimal formation.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Dec;23(12):8482-8492. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14738. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31638340 Free PMC article.
-
CFTR Suppresses Neointimal Formation Through Attenuating Proliferation and Migration of Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 1;79(6):914-924. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001257. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35266910 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Myeloid-derived growth factor in diseases: structure, function and mechanisms.Mol Med. 2024 Jul 19;30(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00874-z. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39030488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 25;25(21):11474. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111474. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

