Patient-reported outcome measures in functional dyspepsia: a systematic review and COSMIN analysis
- PMID: 37726672
- PMCID: PMC10507973
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-023-02935-9
Patient-reported outcome measures in functional dyspepsia: a systematic review and COSMIN analysis
Abstract
Background: Functional dyspepsia (FD) as a type of disorders of brain-gut interaction (DBGI), patient self-reporting of its symptoms becomes an important component of clinical outcome assessment. We performed a systematic review using Consensus Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) guidelines to identify the best available patient-reported outcome measure (PROM) of FD.
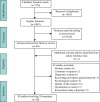
Methods: The study was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). We searched four databases with no date limit, looking for previously confirmed PROMs for evaluating FD symptoms. An overall rating was then assigned based upon COSMIN guidelines, and the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach was used to assess the level of evidence for psychometric properties of included PROMs.
Results: Thirty articles covering outcome indicators of 24 patient reports were included. The Leuven Postprandial Distress Scale (LPDS) showed adequate content validity and moderate quality evidence of adequate internal consistency to generate an A recommendation.
Conclusion: LPDS is currently the most recommended PROM for patient self-reported FD symptoms. However, it fails to assess two important areas of cross-cultural validity/ measurement invariance and measurement error. Future research can be continuously improved on this basis.
Keywords: Dyspepsia; Functional dyspepsia; Measurement properties; Patient-reported outcome measure.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Maternal Postpartum Depression Using the Consensus-Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments Guideline: A Systematic Review.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Jun 1;5(6):e2214885. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.14885. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35749118 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of patient-reported outcome measures to assess postpartum pain using Consensus Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) guidelines.Br J Anaesth. 2021 Aug;127(2):264-274. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.03.035. Epub 2021 May 18. Br J Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 34016441
-
A systematic review of patient-reported outcome measures used to assess sleep in postpartum women using Consensus Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) guidelines.Sleep. 2021 Oct 11;44(10):zsab128. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab128. Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34013345 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures to Assess Outpatient Postpartum Recovery: A Systematic Review.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 May 3;4(5):e2111600. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11600. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34042993 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) for bladder cancer: a systematic review using the COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN) checklist.BJU Int. 2018 Nov;122(5):760-773. doi: 10.1111/bju.14368. Epub 2018 Jun 8. BJU Int. 2018. PMID: 29726085 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fermented Gold Kiwi for Improved Gastric Health: Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety in a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 13;16(16):2670. doi: 10.3390/nu16162670. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203808 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Proton pump inhibitors for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced ulcers and dyspepsia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 8;5(5):CD014585. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014585.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40337979
-
Clinical Reasoning and Practices in the Osteopathic Management of Visceral Disorders: A Grounded Theory Study in the Italian Context.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Aug 14;13(16):1995. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13161995. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taylor F, Reasner DS, Carson RT, et al. Development of a symptom-based patient-reported outcome instrument for functional dyspepsia: a preliminary conceptual model and an evaluation of the adequacy of existing instruments. Patient. 2016;9(5):409–418. doi: 10.1007/s40271-016-0164-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical