Application of mesenchymal stem cells for anti-senescence and clinical challenges
- PMID: 37726805
- PMCID: PMC10510299
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03497-z
Application of mesenchymal stem cells for anti-senescence and clinical challenges
Abstract
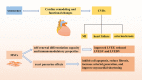
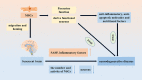
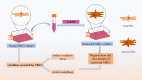
Senescence is a hot topic nowadays, which shows the accumulation of senescent cells and inflammatory factors, leading to the occurrence of various senescence-related diseases. Although some methods have been identified to partly delay senescence, such as strengthening exercise, restricting diet, and some drugs, these only slow down the process of senescence and cannot fundamentally delay or even reverse senescence. Stem cell-based therapy is expected to be a potential effective way to alleviate or cure senescence-related disorders in the coming future. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are the most widely used cell type in treating various diseases due to their potentials of self-replication and multidirectional differentiation, paracrine action, and immunoregulatory effects. Some biological characteristics of MSCs can be well targeted at the pathological features of aging. Therefore, MSC-based therapy is also a promising strategy to combat senescence-related diseases. Here we review the recent progresses of MSC-based therapies in the research of age-related diseases and the challenges in clinical application, proving further insight and reference for broad application prospects of MSCs in effectively combating senesce in the future.
Keywords: Aging; Mesenchymal stromal cells; Regenerative medicine; Senescence; Senescence-related diseases; Stem cells.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

