Greater male variability in daily energy expenditure develops through puberty
- PMID: 37727077
- PMCID: PMC10509569
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2023.0152
Greater male variability in daily energy expenditure develops through puberty
Erratum in
-
Correction: 'Greater male variability in daily energy expenditure develops through puberty' (2023), by Halsey et al.Biol Lett. 2023 Nov;19(11):20230482. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2023.0482. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37909701 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
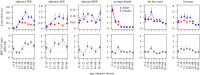
There is considerably greater variation in metabolic rates between men than between women, in terms of basal, activity and total (daily) energy expenditure (EE). One possible explanation is that EE is associated with male sexual characteristics (which are known to vary more than other traits) such as musculature and athletic capacity. Such traits might be predicted to be most prominent during periods of adolescence and young adulthood, when sexual behaviour develops and peaks. We tested this hypothesis on a large dataset by comparing the amount of male variation and female variation in total EE, activity EE and basal EE, at different life stages, along with several morphological traits: height, fat free mass and fat mass. Total EE, and to some degree also activity EE, exhibit considerable greater male variation (GMV) in young adults, and then a decreasing GMV in progressively older individuals. Arguably, basal EE, and also morphometrics, do not exhibit this pattern. These findings suggest that single male sexual characteristics may not exhibit peak GMV in young adulthood, however total and perhaps also activity EE, associated with many morphological and physiological traits combined, do exhibit GMV most prominently during the reproductive life stages.
Keywords: age; height; inter-individual variation; morphometry; weight.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Baye A, Monseur C. 2016. Gender differences in variability and extreme scores in an international context. Large-Scale Assess. Educ. 4, 1. ( 10.1186/s40536-015-0015-x) - DOI
-
- Darwin, C. 1871. The descent of man, and selection in relation to sex. London, UK: John Murray.
-
- Wilmore JH. 1974. Alterations in strength, body composition and anthropometric measurements consequent to a 10-week weight training program. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 6, 133-138. - PubMed
