Reduced biophotonic activities and spectral blueshift in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia models with cognitive impairment
- PMID: 37727319
- PMCID: PMC10505668
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1208274
Reduced biophotonic activities and spectral blueshift in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia models with cognitive impairment
Abstract
Background: Although clinically, Alzheimer's disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VaD) are the two major types of dementia, it is unclear whether the biophotonic activities associated with cognitive impairments in these diseases share common pathological features.
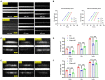
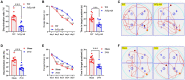
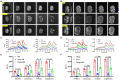
Methods: We used the ultraweak biophoton imaging system (UBIS) and synaptosomes prepared by modified percoll method to directly evaluate the functional changes in synapses and neural circuits in AD and VaD model animals.
Results: We found that biophotonic activities induced by glutamate were significantly reduced and spectral blueshifted in synaptosomes and brain slices. These changes could be partially reversed by pre-perfusion of the ifenprodil, a specific antagonist of the GluN2B subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that AD and VaD pathology present similar but complex changes in biophotonic activities and transmission at synapses and neural circuits, implying that communications and information processing of biophotonic signals in the brain are crucial for advanced cognitive functions.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biophotonic activity; cognitive impairment; spectral blueshift; synaptic dysfunction; synaptosome; vascular dementia.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Xu, Luo, Peng, Song, Li, Zheng, Liu, Wu, Zhang, Zhang, Hu, Liu, Lu, Dai and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spectral blueshift of biophotonic activity and transmission in the ageing mouse brain.Brain Res. 2020 Dec 15;1749:147133. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147133. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32971084
-
Human high intelligence is involved in spectral redshift of biophotonic activities in the brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 2;113(31):8753-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604855113. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27432962 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal imaging of glutamate-induced biophotonic activities and transmission in neural circuits.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 15;9(1):e85643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085643. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24454909 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and management of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia.J Neural Transm Suppl. 2002;(63):91-109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6137-1_6. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12597611 Review.
-
Dysfunctional synapse in Alzheimer's disease - A focus on NMDA receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt A:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.013. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23973316 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential involvement of central and peripheral catecholamines between Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 2;10(19):e38843. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38843. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39398044 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

