Imidacloprid Induces Neurotoxicity in Albino Male Rats by Inhibiting Acetylcholinesterase Activity, Altering Antioxidant Status, and Primary DNA Damage
- PMID: 37727350
- PMCID: PMC10506876
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/4267469
Imidacloprid Induces Neurotoxicity in Albino Male Rats by Inhibiting Acetylcholinesterase Activity, Altering Antioxidant Status, and Primary DNA Damage
Abstract
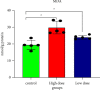
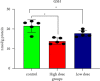
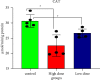
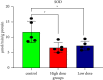
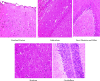
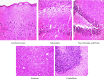
Imidacloprid (IMI) is a neonicotinoid insecticide used worldwide, either alone or in combination with other pesticides. The goal of this study was to assess the effects of IMI on the central nervous system of rats and its mechanism of oxidative stress-induced DNA damage by oxidant/antioxidant parameters. Fifteen male rats, divided into three groups, were used: the first group received 5 ml/kg body weight corn oil as a control, the second received a high oral dose of IMI (45 mg/kg body weight), while the third received a low dose (22 mg/kg body weight). After 28 days, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, oxidative stress markers, histopathological alterations, and DNA damage were examined in the brains of these rats. The AChE activities decreased significantly after IMI exposure, reaching 2.45 and 2.75 nmol/min/mg protein in high dose and low dose, respectively, compared to the control group (3.75 nmol/g tissues), while the concentration of malondialdehyde MDA increased significantly (29.28 and 23.92 nmol/g tissues) vs. the control group (19.28 nmol/g tissues). The antioxidant status parameters such as reduced glutathione (GSH) content was 13.77 and 17.63 nmol/g, catalase (CAT) activity was 22.56 and 26.65 µmol/min/g, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was 6.66 and 7.23 µmol/min/g in both doses against the control group (21.37 nmol/g, 30.67 µmol/min/g, 11.76 µmol/min/g), respectively, and histopathological changes in the brain tissues were observed. More in vivo research using epigenetic methods is needed to determine the ability of IMI and its metabolites to cause neurotoxicity and DNA lesions in mammalian brains.
Copyright © 2023 Hossam El Din H. Abdelhafez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HA, FH, AE, and JG declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lysosomal disruption, mitochondrial impairment, histopathological and oxidative stress in rat's nervous system after exposure to a neonicotinoid (imidacloprid).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Oct;31(49):59472-59489. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-35195-5. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39356435
-
Protective action of polysaccharides from Laurencia papillose (Rhodophyta) against imidacloprid induced genotoxicity and oxidative stress in male albino rats.Environ Anal Health Toxicol. 2022 Jun;37(2):e2022011-0. doi: 10.5620/eaht.2022011. Epub 2022 May 10. Environ Anal Health Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35878919 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-related impacts of imidacloprid oral intoxication on brain and liver of rock pigeon (Columba livia domestica), residues analysis in different organs.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Jan 15;167:60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.121. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019. PMID: 30296697
-
Toxic effects of imidacloprid combined with arsenic: Oxidative stress in rat liver.Toxicol Ind Health. 2018 Oct;34(10):726-735. doi: 10.1177/0748233718778993. Epub 2018 Jul 22. Toxicol Ind Health. 2018. PMID: 30033815
-
Chemoprotective role of ethanol extract of Urtica urens L. against the toxicity of imidacloprid on endocrine disruption and ovarian morphometric in female rats, GC/MS analysis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:518-527. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.150. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29091903
Cited by
-
The potential neuroprotective of luteolin against acetamiprid-induced neurotoxicity in the rat cerebral cortex.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 2;11:1361792. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1361792. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38818490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tomizawa M., Zhang N., Durkin K. A., Olmstead M. M., Casida J. E. The neonicotinoid electronegative pharmacophore plays the crucial role in the high affinity and selectivity for the Drosophila nicotinic receptor: an anomaly for the nicotinoid cation− π interaction model. Biochemistry . 2003;42(25):7819–7827. doi: 10.1021/bi0300130. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guerra L. J., do Amaral A. M. B., de Quadros V. A., et al. Biochemical and behavioral responses in zebrafish exposed to imidacloprid oxidative damage and antioxidant responses. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology . 2021;81(2):255–264. doi: 10.1007/s00244-021-00865-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

