Acoustic Noise Levels in High-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners
- PMID: 37727400
- PMCID: PMC10506133
- DOI: 10.1002/oto2.79
Acoustic Noise Levels in High-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scanners
Abstract
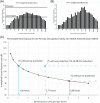
7-Tesla (T) magnetic resonance imaging may allow for higher resolution images but may produce greater acoustic noise than 1.5- and 3-T scanners. We sought to characterize the intensity of acoustic noise from 7- versus 3-T scanners. A-weighted sound pressure levels from 5 types of pulse sequences used for brain and inner ear imaging in 3- and 7-T scanners were measured. Time-averaged sound level and maximum sound levels generated for each sequence were compared. Time-averaged sound levels exceeded 95 dB and reached maximums above 105 dB on the majority of 3- and 7-T scans. The mean time-averaged sound level and maximum sound level across pulse sequences were greater in 7- than 3-T (105.6 vs 91.4, P = .01; 114.0 vs. 96.5 dB, P < .01). 7- and 3-T magnetic resonance imaging scanners produce high levels of acoustic noise that exceed acceptable safety limits, emphasizing the need for active and passive noise protection.
Keywords: 3‐Tesla MRI; 7‐Tesla MRI; acoustic noise; brain imaging; inner ear imaging.
© 2023 The Authors. OTO Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measurement and evaluation of the acoustic noise of a 3 Tesla MR scanner.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2007 Jan;69(1-2):23-8. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 17378177
-
Relationship between magnetic field strength and magnetic-resonance-related acoustic noise levels.MAGMA. 2003 Feb;16(1):52-5. doi: 10.1007/s10334-003-0005-9. MAGMA. 2003. PMID: 12695886
-
Investigation of acoustic noise on 15 MRI scanners from 0.2 T to 3 T.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001 Feb;13(2):288-93. doi: 10.1002/1522-2586(200102)13:2<288::aid-jmri1041>3.0.co;2-p. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001. PMID: 11169836
-
3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging noise in standard head and neck sequence does not cause temporary threshold shift in high frequency.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Nov;272(11):3109-13. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3232-y. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25205300 Review.
-
Geographical mapping and modelling of noise pollution from industrial motors: a case study of the Mbalmayo Thermal Power Plant in Cameroon.Environ Monit Assess. 2019 Nov 21;191(12):765. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7940-z. Environ Monit Assess. 2019. PMID: 31754865 Review.
Cited by
-
A closer look: pediatric neuroimaging at 7T.Pediatr Radiol. 2025 May;55(6):1071-1087. doi: 10.1007/s00247-025-06231-4. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Pediatr Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40257498 Review.
-
Exploring the Relationship between Behavioral and Neurological Impairments Due to Mild Cognitive Impairment: Correlation Study between Virtual Kiosk Test and EEG-SSVEP.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 30;24(11):3543. doi: 10.3390/s24113543. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894334 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Software-Optimized Protocols for Acoustic Noise Reduction During Brain MRI at 7 Tesla.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Aug;62(2):577-587. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29749. Epub 2025 Mar 6. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40048635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Wilde J, Grainger D, Price DL, Renaud C. Magnetic resonance imaging safety issues including an analysis of recorded incidents within the UK. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2007;51(1):12. 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2007.01.003 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

