Mechanism and recent updates on insulin-related disorders
- PMID: 37727490
- PMCID: PMC10506040
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5840
Mechanism and recent updates on insulin-related disorders
Abstract
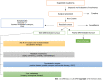
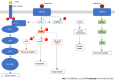
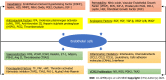
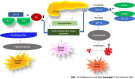
Insulin, a small protein with 51 amino acids synthesized by pancreatic β-cells, is crucial to sustain glucose homeostasis at biochemical and molecular levels. Numerous metabolic dysfunctions are related to insulin-mediated altered glucose homeostasis. One of the significant pathophysiological conditions linked to the insulin associated disorder is diabetes mellitus (DM) (type 1, type 2, and gestational). Insulin resistance (IR) is one of the major underlying causes of metabolic disorders despite its association with several physiological conditions. Metabolic syndrome (MS) is another pathophysiological condition that is associated with IR, hypertension, and obesity. Further, several other pathophysiological disorders/diseases are associated with the insulin malfunctioning, which include polycystic ovary syndrome, neuronal disorders, and cancer. Insulinomas are an uncommon type of pancreatic β-cell-derived neuroendocrine tumor that makes up 2% of all pancreatic neoplasms. Literature revealed that different biochemical events, molecular signaling pathways, microRNAs, and microbiota act as connecting links between insulin disorder and associated pathophysiology such as DM, insuloma, neurological disorder, MS, and cancer. In this review, we focus on the insulin-related disorders and the underlying mechanisms associated with the pathophysiology.
Keywords: Cancer; Diabetes; Insulin disorder; Metabolic syndrome; Neurological disorder; Obesity.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Vander Mierde D, Scheuner D, Quintens R, Patel R, Song B, Tsukamoto K, Beullens M, Kaufman RJ, Bollen M, Schuit FC. Glucose activates a protein phosphatase-1-mediated signaling pathway to enhance overall translation in pancreatic beta-cells. Endocrinology. 2007;148:609–617. - PubMed
-
- Suckale J, Solimena M. Pancreas islets in metabolic signaling--focus on the beta-cell. Front Biosci. 2008;13:7156–7171. - PubMed
-
- Chang TW, Goldberg AL. The metabolic fates of amino acids and the formation of glutamine in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1978;253:3685–3693. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

