Smarca4 deficiency induces Pttg1 oncogene upregulation and hyperproliferation of tubular and interstitial cells during kidney development
- PMID: 37727504
- PMCID: PMC10506413
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1233317
Smarca4 deficiency induces Pttg1 oncogene upregulation and hyperproliferation of tubular and interstitial cells during kidney development
Abstract
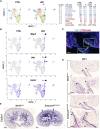
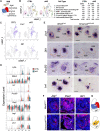
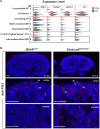
Kidney formation and nephrogenesis are controlled by precise spatiotemporal gene expression programs, which are coordinately regulated by cell-cycle, cell type-specific transcription factors and epigenetic/chromatin regulators. However, the roles of epigenetic/chromatin regulators in kidney development and disease remain poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the impact of deleting the chromatin remodeling factor Smarca4 (Brg1), a human Wilms tumor-associated gene, in Wnt4-expressing cells. Smarca4 deficiency led to severe tubular defects and a shortened medulla. Through unbiased single-cell RNA sequencing analyses, we identified multiple types of Wnt4 Cre-labeled interstitial cells, along with nephron-related cells. Smarca4 deficiency increased interstitial cells but markedly reduced tubular cells, resulting in cells with mixed identity and elevated expression of cell-cycle regulators and genes associated with extracellular matrix and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition/fibrosis. We found that Smarca4 loss induced a significant upregulation of the oncogene Pttg1 and hyperproliferation of Wnt4 Cre-labeled cells. These changes in the cellular state could hinder the cellular transition into characteristic tubular structures, eventually leading to fibrosis. In conclusion, our findings shed light on novel cell types and genes associated with Wnt4 Cre-labeled cells and highlight the critical role of Smarca4 in regulating tubular cell differentiation and the expression of the cancer-causing gene Pttg1 in the kidney. These findings may provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic strategies for renal cell carcinoma resulting from SMARCA4 deficiency.
Keywords: Pttg1; SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex; Smarca4/Brg1; Wnt4; fibrosis; nephron tubulogenesis; renal interstitium.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Zhou, Zhang, Zhang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex status in renal cell carcinomas with sarcomatoid or rhabdoid features.Virchows Arch. 2020 Nov;477(5):651-660. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-02839-z. Epub 2020 May 23. Virchows Arch. 2020. PMID: 32447490
-
SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling subunit Smarca4/BRG1 is essential for female fertility†.Biol Reprod. 2023 Feb 13;108(2):279-291. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioac209. Biol Reprod. 2023. PMID: 36440965 Free PMC article.
-
Switch/sucrose-non-fermentable (SWI/SNF) complex (SMARCA4, SMARCA2, INI1/SMARCB1)-deficient colorectal carcinomas are strongly associated with microsatellite instability: an incidence study in 4508 colorectal carcinomas.Histopathology. 2022 May;80(6):906-921. doi: 10.1111/his.14612. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Histopathology. 2022. PMID: 34951482
-
SWI/SNF complex-deficient soft tissue neoplasms: An update.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2021 May;38(3):222-231. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32646614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent updates in thoracic SMARCA4-deficient undifferentiated tumor.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2021 Sep;38(5):83-89. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34147303 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the role of key gene PTTG1 in clear cell renal carcinoma based on bioinformatics analysis and In-vitro cell experiments.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Jun 17;14(3):tfaf078. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf078. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40585419
References
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate - a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B-Methodological 57 (1), 289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

