In-vitro and computational analysis of Urolithin-A for anti-inflammatory activity on Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2)
- PMID: 37727526
- PMCID: PMC10505678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103804
In-vitro and computational analysis of Urolithin-A for anti-inflammatory activity on Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2)
Abstract
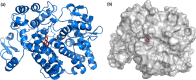
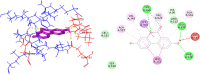
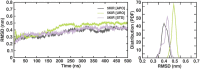
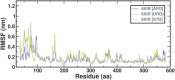
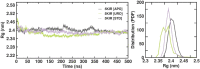
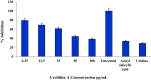
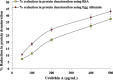
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) participates in the inflammation process by converting arachidonic acid into prostaglandin G2 which increases inflammation, pain and fever. COX-2 has an active site and a heme pocket and blocking these sites stops the inflammation. Urolithin A is metabolite of ellagitannin produced from humans and animals gut microbes. In the current study, Urolithin A showed good pharmacokinetic properties. Molecular docking of the complex of Urolithin A and COX-2 revealed the ligand affinity of -7.97 kcal/mol with the ligand binding sites at TYR355, PHE518, ILE517 and GLN192 with the 4-H bonds at a distance of 2.8 Å, 2.3 Å, 2.5 Å and 1.9 Å. The RMSD plot for Urolithin A and COX-2 complex was observed to be constant throughout the duration of dynamics. A total of 3 pair of hydrogen bonds was largely observed on average of 3 simulation positions for dynamics duration of 500 ns. The MMPBSA analysis showed that active site amino acids had a binding energy of -22.0368 kJ/mol indicating that throughout the simulation the protein of target was bounded by Urolithin A. In-silico results were validated by biological assays. Urolithin A strongly revealed to exhibit anti-inflammatory effect on COX-2 with an IC50 value of 44.04 µg/mL. The anti-inflammatory capability was also depicted through reduction of protein denaturation that showed 37.6 ± 0.1 % and 43.2 ± 0.07 % reduction of protein denaturation for BSA and egg albumin respectively at 500 µg/mL. The present study, suggests Urolithin A to be an effective anti-inflammatory compound for therapeutic use.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Cyclo-oxygenase 2; Molecular Dynamics simulation; Urolithin A.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Ahmad V. A molecular docking study against COVID-19 protease with a pomegranate phyto-constituents “Urolithin” and other repurposing drugs: from a supplement to ailment. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2020:51–62. doi: 10.9734/jpri/2020/v32i1130545. - DOI
-
- Ahsan A., Zheng Y., Wu X., Tang W., Liu M., Ma S., Jiang L., Hu W., Zhang X., Chen Z. Urolithin A-activated autophagy but not mitophagy protects against ischemic neuronal injury by inhibiting ER stress in vitro and in vivo. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019;25:976–986. doi: 10.1111/cns.13136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akhter S., Irfan H.M., Alamgeer U.A., Jahan S., Roman M., Latif M.B., Mustafa Z., Almutairi F.M., Althobaiti Y.S. Noscapine hydrochloride (benzyl-isoquinoline alkaloid) effectively prevents protein denaturation through reduction of IL-6, NF-kB, COX-2, Prostaglandin-E2 in rheumatic rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022;30:1791–1801. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.10.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alam A., Jawaid T., Alam P. In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of green cardamom essential oil and in silico molecular docking of its major bioactives. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2021;15:757–768. doi: 10.1080/16583655.2021.2002550. - DOI
-
- Araújo P.H.F., Ramos R.S., da Cruz J.N., Silva S.G., Ferreira E.F.B., de Lima L.R., Macêdo W.J.C., Espejo-Román J.M., Campos J.M., Santos C.B.R. Identification of potential COX-2 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases using molecular modeling approaches. Molecules. 2020;25:4183. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184183. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

