Formulation and optimization of ivermectin nanocrystals for enhanced topical delivery
- PMID: 37727680
- PMCID: PMC10506092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2023.100210
Formulation and optimization of ivermectin nanocrystals for enhanced topical delivery
Abstract
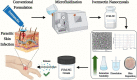
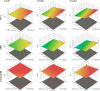
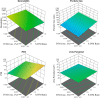
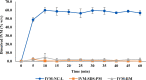
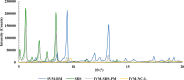
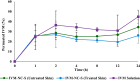
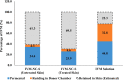
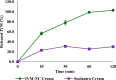
The increasing resistance to antiparasitic drugs and limited availability of new agents highlight the need to improve the efficacy of existing treatments. Ivermectin (IVM) is commonly used for parasite treatment in humans and animals, however its efficacy is not optimal and the emergence of IVM-resistant parasites presents a challenge. In this context, the physico-chemical characteristics of IVM were modified by nanocrystallization to improve its equilibrium water-solubility and skin penetration, potentially improving its therapeutic effectiveness when applied topically. IVM-nanocrystals (IVM-NC) were prepared using microfluidization technique. The impact of several process/formulation variables on IVM-NC characteristics were studied using D-optimal statistical design. The optimized formulation was further lyophilized and evaluated using several in vitro and ex vivo tests. The optimal IVM-NC produced monodisperse particles with average diameter of 186 nm and polydispersity index of 0.4. In vitro results showed an impressive 730-fold increase in the equilibrium solubility and substantial 24-fold increase in dissolution rate. Ex vivo permeation study using pig's ear skin demonstrated 3-fold increase in dermal deposition of IVM-NC. Additionally, lyophilized IVM-NC was integrated into topical cream, and the resulting drug release profile was superior compared to that of the marketed product. Overall, IVM-NC presents a promising approach to improving the effectiveness of topically applied IVM in treating local parasitic infections.
Keywords: Antiparasitic; Dermal drug delivery; Ivermectin; Nanocrystal; Quality by design (QBD); Skin.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Optimization, characterization and in vivo evaluation of mupirocin nanocrystals for topical administration.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Sep 1;176:106251. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106251. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35788029
-
Nanocrystals of Fusidic Acid for Dual Enhancement of Dermal Delivery and Antibacterial Activity: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Feb 25;12(3):199. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12030199. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32106544 Free PMC article.
-
Design and in vitro characterization of ivermectin nanocrystals liquid formulation based on a top-down approach.Pharm Dev Technol. 2017 Sep;22(6):809-817. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2016.1200078. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Pharm Dev Technol. 2017. PMID: 27346432
-
Ivermectin: From theory to clinical application.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019 Aug;54(2):134-142. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 May 7. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019. PMID: 31071469 Review.
-
Repurposing Potential of the Antiparasitic Agent Ivermectin for the Treatment and/or Prophylaxis of COVID-19.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 27;15(9):1068. doi: 10.3390/ph15091068. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental study on the effect of Ivermectin on cattle dung faunas in Eastern Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 16;20(4):e0320867. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320867. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40238803 Free PMC article.
-
Maximizing the Use of Ivermectin Transethosomal Cream in the Treatment of Scabies.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 1;16(8):1026. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081026. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204371 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Investigation into the Design, Optimization, Toxicity, and Anti-Viral Efficacy of Proliposomes Loaded with Ivermectin Against Infectious Bronchitis Virus Using an Embryonated Chicken Egg Model.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jan 25;17(2):165. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020165. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006532 Free PMC article.
-
3D-printed Laponite/Alginate hydrogel-based suppositories for versatile drug loading and release.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Dec;14(12):3385-3403. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01506-5. Epub 2024 Jan 7. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38185776 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Topical and Transdermal Drug Delivery Research-Focus on Nanoformulations.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 16;16(6):817. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060817. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

