Effect of pesticides on phosphorylation of tau protein, and its influence on Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37727721
- PMCID: PMC10506003
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i24.5628
Effect of pesticides on phosphorylation of tau protein, and its influence on Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
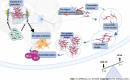
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive and neurodegenerative illness which results in alterations in cognitive development. It is characterized by loss/dysfunction of cholinergic neurons, and formation of amyloid plaques, and formation of neurofibrillary tangles, among other changes, due to hyperphosphorylation of tau-protein. Exposure to pesticides in humans occurs frequently due to contact with contaminated food, water, or particles. Organochlorines, organophosphates, carbamates, pyrethroids and neonicotinoids are associated with the most diagnosed incidents of severe cognitive impairment. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of these pesticides on the phosphorylation of tau protein, and its cognitive implications in the development of AD. It was found that exposure to pesticides increased the phosphorylation of tau protein at sites Ser198, Ser199, Ser202, Thr205, Ser396 and Ser404. Contact with these chemicals altered the enzymatic activities of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta, and protein phosphatase-2A. Moreover, it altered the expression of the microtubule associated protein tau gene, and changed levels of intracellular calcium. These changes affected tau protein phosphorylation and neuroinflammation, and also increased oxidative stress. In addition, the exposed subjects had poor level of performance in tests that involved evaluation of novelty, as test on verbal, non-verbal, spatial memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
Keywords: Carbamates; Neonicotinoids; Organochlorines; Organophosphates; Pyrethroids; Tau protein.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Dementia. [cited 20 March 2023]. Available from: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia .
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. Dementia statistics. [cited 6 April 2023]. Available from: https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/dementia-statistics/
-
- 2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19:1598–1695. - PubMed
-
- Eldin Bayoumi A. Deleterious effects of banned chemical pesticides on human health in developing countries. In: Larramendy LM, Soloneski S. Pesticides - Updates on Toxicity, Efficacy and Risk Assessment. London: IntechOpen, 2022.
-
- Shah R. Pesticides and human health. In: Nuro A. Emerging contaminants. London: IntechOpen, 2021.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

