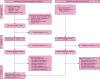
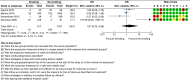
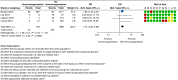
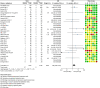
Midline incisional hernia guidelines: the European Hernia Society
- PMID: 37727928
- PMCID: PMC10638550
- DOI: 10.1093/bjs/znad284
Midline incisional hernia guidelines: the European Hernia Society
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Midline incisional hernia guidelines: the European Hernia Society.Br J Surg. 2024 Jan 3;111(1):znad349. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znad349. Br J Surg. 2024. PMID: 37881845 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Figures














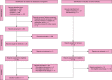



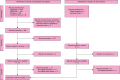
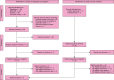


References
-
- Bloemen A, van Dooren P, Huizinga BF, Hoofwijk AG. Comparison of ultrasonography and physical examination in the diagnosis of incisional hernia in a prospective study. Hernia 2012;16:53–57 - PubMed
-
- Claes K, Beckers R, Heindryckx E, Kyle-Leinhase I, Pletinckx P, Claeys Det al. Retrospective observational study on the incidence of incisional hernias after colorectal carcinoma resection with follow-up CT scan. Hernia 2014;18:797–802 - PubMed
-
- den Hartog D, Dur AHM, Kamphuis AGA, Tuinebreijer WE, Kreis RW. Comparison of ultrasonography with computed tomography in the diagnosis of incisional hernias. Hernia 2009;13:45–48 - PubMed
-
- Diener MK, Voss S, Jensen K, Buchler MW, Seiler CM. Elective midline laparotomy closure: the INLINE systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 2010;251:843–856 - PubMed
-
- Fink C, Baumann P, Wente MN, Knebel P, Bruckner T, Ulrich Aet al. Incisional hernia rate 3 years after midline laparotomy. Br J Surg 2014;101:51–54 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

