Population pharmacokinetic analysis of enrofloxacin and its active metabolite ciprofloxacin after intravenous injection to cats with reduced kidney function
- PMID: 37728198
- PMCID: PMC10658592
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.16866
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of enrofloxacin and its active metabolite ciprofloxacin after intravenous injection to cats with reduced kidney function
Abstract
Background: It is unknown if enrofloxacin accumulates in plasma of cats with reduced kidney function.
Hypothesis: To determine if enrofloxacin and its active metabolite ciprofloxacin have reduced clearance in azotemic cats.
Animals: Thirty-four cats hospitalized for clinical illness with variable degree of kidney function.
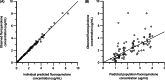
Methods: Prospective study. After enrofloxacin (dose 5 mg/kg) administration to cats, sparse blood sampling was used to obtain 2 compartment population pharmacokinetic results using nonlinear mixed-effects modeling. Plasma enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin concentrations were measured and summed to obtain the total fluoroquinolone concentration. A model of ciprofloxacin metabolism from enrofloxacin was created and evaluated for covariate effects on clearance, volume of distribution, and the metabolic rate of ciprofloxacin generation from enrofloxacin.
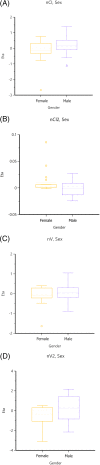
Results: Body weight was the only covariate found to affect total fluoroquinolone volume of distribution (effect 1.63, SE 0.19, P < .01) and clearance (effect 1.63, SE 0.27, P < .01). Kidney function did not have a significant effect on total fluoroquinolone clearance (median 440.8 mL/kg/h (range 191.4-538.0 mL/kg/h) in cats with normal kidney function, 365.8 mL/kg/h (range 89.49-1092.0 mL/kg/h) in cats with moderate kidney dysfunction, and 308.5 mL/kg/h (range 140.20-480.0 mL/kg/h) in cats with severe kidney dysfunction (P = .64). Blood urea nitrogen concentration influenced the metabolic generation of ciprofloxacin from enrofloxacin (effect 0.51, SE 0.08, P < .01), but other markers of kidney function did not.
Conclusions and clinical importance: Adjustment of enrofloxacin dosage is not indicated for azotemic cats.
Keywords: drug prescribing; feline; fluroquinolone; renal failure.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Jonathan D Foster is a board member of the International Renal Interest Society and an advisory board member for Elanco. His participation in the Elanco advisory board began after oral presentation of this research and did not overlap when the research was performed. Mahmoud Abouraya is an employee of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The information in these materials is not a formal dissemination of information by FDA and does not constitute an advisory opinion, does not necessarily represent the formal position of FDA, and does not bind or otherwise obligate or commit the agency to the views expressed. This collaboration should not be construed as FDA endorsement or preference for a company or specific modeling software. This study was not used for FDA drug approval. Mark G Papich is a current member, and former chair holder of the CLSI‐VAST subcommittee. No other authors declare a conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Population pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin in chicken based on retrospective data, incorporating first-pass metabolism.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Feb;33(1):84-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2009.01106.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20444030
-
Pharmacokinetic variables and tissue residues of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in healthy pigs.Am J Vet Res. 1999 Nov;60(11):1377-82. Am J Vet Res. 1999. PMID: 10566812
-
Effects of endotoxin-induced fever and probenecid on disposition of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin after intravascular administration of enrofloxacin in goats.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Dec;23(6):365-72. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2885.2000.00295.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 11168914
-
Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin after intravenous and oral administration of enrofloxacin in dogs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Dec;16(4):462-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.1993.tb00212.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1993. PMID: 8126763
-
Fluoroquinolone-induced retinal degeneration in cats.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2002 Dec 1;221(11):1568-71. doi: 10.2460/javma.2002.221.1568. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2002. PMID: 12479325 Review.
Cited by
-
Bridging one health and sustainable analysis: enrofloxacin quantification amid combined therapy and its active metabolite in various matrices using green RP-HPLC.BMC Chem. 2024 Sep 19;18(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01283-3. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 39300544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finco DR, Barsanti JA. Bacterial pyelonephritis. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1980;9(4):645‐660. - PubMed
-
- DiBartola SP, Rutgers HC, Zack PM, Tarr MJ. Clinicopathologic findings associated with chronic renal disease in cats: 74 cases (1973‐1984). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1987;190(9):1196‐1202. - PubMed
-
- Weese JS, Blondeau J, Boothe D, et al. International Society for Companion Animal Infectious Diseases (ISCAID) guidelines for the diagnosis and management of bacterial urinary tract infections in dogs and cats. Vet J. 2019;247:8‐25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

