Nameability supports rule-based category learning in children and adults
- PMID: 37728552
- PMCID: PMC10922161
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.14008
Nameability supports rule-based category learning in children and adults
Abstract
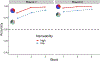
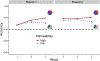
The present study tested the hypothesis that verbal labels support category induction by providing compact hypotheses. Ninety-seven 4- to 6-year-old children (M = 63.2 months; 46 female, 51 male; 77% White, 8% more than one race, 4% Asian, and 3% Black; tested 2018) and 90 adults (M = 20.1 years; 70 female, 20 male) in the Midwestern United States learned novel categories with features that were easy (e.g., "red") or difficult (e.g., "mauve") to name. Adults (d = 1.06) and-to a lesser extent-children (d = 0.57; final training block) learned categories composed of more nameable features better. Children's knowledge of difficult-to-name color words predicted their learning for categories with difficult-to-name features. Rule-based category learning may be supported by the emerging ability to form verbal hypotheses.
© 2023 The Authors. Child Development published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Society for Research in Child Development.
Figures


References
-
- Baayen RH, Davidson DJ, & Bates DM (2008). Mixed-effects modeling with crossed random effects for subjects and items. Journal of Memory and Language, 59, 390–412. 10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.005 - DOI
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker BM, & Walker SC (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
