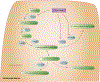
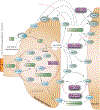
PharmGKB summary: disulfiram pathway
- PMID: 37728645
- PMCID: PMC10627108
- DOI: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000509
PharmGKB summary: disulfiram pathway
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures



References
-
- Stokes M, Abdijadid S. Disulfiram. In: StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL) (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

