Updated guidelines for chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease
- PMID: 37728704
- PMCID: PMC10615970
- DOI: 10.1007/s12185-023-03660-5
Updated guidelines for chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease
Abstract
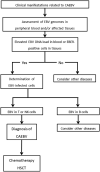
Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease (CAEBV), formerly named chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection, is characterized by systemic inflammation and clonal proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected T or NK cells. As CAEBV is a potentially life-threatening illness, appropriate diagnosis and therapeutic interventions are necessary for favorable clinical outcomes. Substantial evidence regarding the pathogenesis and treatment of CAEBV has been accumulated since previous guidelines for the diagnosis of CAEBV were proposed. To reflect this evidence, we updated the guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of CAEBV to improve clinical management of the disease. The details of the updated guidelines are presented in this report. Diagnosis of CAEBV now requires confirmation of a high copy number of EBV genome and EBV-infected T or NK cells. An EBV DNA load ≥ 10,000 IU/mL in whole blood is proposed as the diagnostic cutoff value for CAEBV in this updated guideline. A standard treatment approach for CAEBV has not been established, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is considered the only curative treatment. Chemotherapy can be administered to control disease activity before HSCT.
Keywords: CAEBV; Diagnostic criteria; EBV; Guidelines.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hirai Y, Asada H, Hamada T, Kawada JI, Kimura H, Arai A, et al. Diagnostic and disease severity determination criteria for hydroa vacciniforme lymphoproliferative disorders and severe mosquito bite allergy. J Dermatol. 2023;50(7):e198–e205. - PubMed
-
- Li W. The 5(th) edition of the World Health Organization classification of hematolymphoid tumors. In: Li W, editor. Leukemia. Brisbane (AU): Exon Publications; 2022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials