ABCA4 Variant c.5714+5G>A in Trans With Null Alleles Results in Primary RPE Damage
- PMID: 37728905
- PMCID: PMC10516765
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.64.12.33
ABCA4 Variant c.5714+5G>A in Trans With Null Alleles Results in Primary RPE Damage
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the disease pathogenesis associated with the frequent ABCA4 variant c.5714+5G>A (p.[=,Glu1863Leufs*33]).
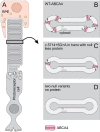
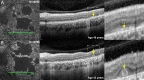
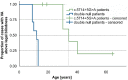
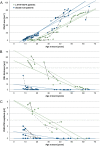
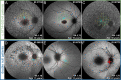
Methods: Patient-derived photoreceptor precursor cells were generated to analyze the effect of c.5714+5G>A on splicing and perform a quantitative analysis of c.5714+5G>A products. Patients with c.5714+5G>A in trans with a null allele (i.e., c.5714+5G>A patients; n = 7) were compared with patients with two null alleles (i.e., double null patients; n = 11); with a special attention to the degree of RPE atrophy (area of definitely decreased autofluorescence and the degree of photoreceptor impairment (outer nuclear layer thickness and pattern electroretinography amplitude).
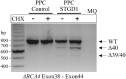
Results: RT-PCR of mRNA from patient-derived photoreceptor precursor cells showed exon 40 and exon 39/40 deletion products, as well as the normal transcript. Quantification of products showed 52.4% normal and 47.6% mutant ABCA4 mRNA. Clinically, c.5714+5G>A patients displayed significantly better structural and functional preservation of photoreceptors (thicker outer nuclear layer, presence of tubulations, higher pattern electroretinography amplitude) than double null patients with similar degrees of RPE loss, whereas double null patients exhibited signs of extensive photoreceptor ,damage even in the areas with preserved RPE.
Conclusions: The prototypical STGD1 sequence of events of primary RPE and secondary photoreceptor damage is congruous with c.5714+5G>A, but not the double null genotype, which implies different and genotype-dependent disease mechanisms. We hypothesize that the relative photoreceptor sparing in c.5714+5G>A patients results from the remaining function of the ABCA4 transporter originating from the normally spliced product, possibly by decreasing the direct bisretinoid toxicity on photoreceptor membranes.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures




References
-
- Blacharski PA. Fundus flavimaculatus. In: Newsome DA, (ed). Retinal Dystrophies and Degenerations. New York: Raven Press; 1988: 135–159.
-
- Molday LL, Rabin AR, Molday RS.. ABCR expression in foveal cone photoreceptors and its role in Stargardt macular dystrophy. Nat Genet . 2000; 25(3): 257–258. - PubMed
-
- Illing M, Molday LL, Molday RS.. The 220-kDa rim protein of retinal rod outer segments is a member of the ABC transporter superfamily. J Biol Chem . 1997; 272(15): 10303–10310. - PubMed
-
- Sun H, Nathans J.. Stargardt's ABCR is localized to the disc membrane of retinal rod outer segments. Nat Genet . 1997; 17(1): 15–16. - PubMed
-
- Papermaster DS, Converse CA, Zorn M.. Biosynthetic and immunochemical characterization of large protein in frog and cattle rod outer segment membranes. Exp Eye Res . 1976; 23(2): 105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

