Diabetes mellitus drug discovery: insights into targeting feline and human amylin with small molecules
- PMID: 37729105
- PMCID: PMC10557562
- DOI: 10.1080/01652176.2023.2260442
Diabetes mellitus drug discovery: insights into targeting feline and human amylin with small molecules
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a health concern for both humans and cats, with cases rising over the past decade. Around 70% of patients from either species exhibit pancreatic aggregates of islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), a protein that proves toxic upon misfolding. These misfolded protein aggregates congregate in the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, diminishing the capability of β-cells to produce insulin and further perpetuating disease.
Objective: Our team's drug discovery program is investigating newly synthesized compounds that could diminish aggregates of both human and feline IAPP, potentially disrupting the progression of T2D.
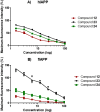
Material and methods: We prepared 24 compounds derived from diaryl urea, as ureas have previously demonstrated great potential at reducing accumulations of misfolded proteins. Biophysical methods were employed to analyze the anti-aggregation activity of these compounds at inhibiting and/or disrupting IAPP fibril formation in vitro.
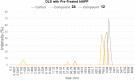
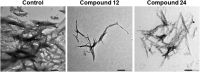
Results: The results demonstrate that compounds 12 and 24 were most effective at reducing the fibrillization and aggregation of both human and feline IAPP. When compared with the control for each experiment, samples treated with either compound 12 or 24 exhibited fewer accumulations of amyloid-like fibrils.
Conclusion: Urea-based compounds, such as compounds 12 and 24, may prove crucial in future pre-clinical studies in the search for therapeutics for T2D.
Keywords: Amylin; cat; drug discovery; islet amyloid polypeptide; pancreatic amyloidosis; small molecule therapeutics; type 2 diabetes; veterinary medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Betsholtz C, Christmanson L, Engström U, Rorsman F, Jordan K, O’Brien TD, Murtaugh M, Johnson KH, Westermark P.. 1990. Structure of cat islet amyloid polypeptide and identification of amino acid residues of potential significance for islet amyloid formation. Diabetes. 39(1):118–122. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.118. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Betsholtz C, Christmansson L, Engström U, Rorsman F, Svensson V, Johnson KH, Westermark P.. 1989. Sequence divergence in a specific region of islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) explains differences in islet amyloid formation between species. FEBS Lett. 251(1-2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81467-x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
