Environmental neurodevelopment toxicity from the perspective of Bronfenbrenner's bioecological model: a case study of toxic metals
- PMID: 37729303
- PMCID: PMC10513156
- DOI: 10.1590/0102-311XEN202022
Environmental neurodevelopment toxicity from the perspective of Bronfenbrenner's bioecological model: a case study of toxic metals
Abstract
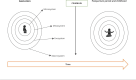
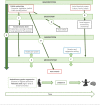
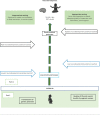
A growing body of literature reports the need for an integrated approach to study the effects of the physical environment on the neurodevelopment of children. Assessment of the true neurotoxicity of pollutants cannot be performed separately from the ecological and multidimensional contexts in which they act. In this study, from the perspective of the Bronfenbrenner's bioecological model, a conceptual model was developed that encompasses the social and biological characteristics of children from the gestational period to childhood, considering exposure to toxic metals. First, we present the toxicity of the main metals and some concept notions that we used in our framework, such as social and structural determinants of health, allostatic load, embodiment, and epigenetic concepts. Then, the main aspects of the Bronfenbrenner's bioecological model, which allow integration of the gene-social relationship in addition to the physical environment, where these metals act, are explained. Finally, we present and discuss the conceptual framework showing how, in real life, biological and social factors may together influence the neurodevelopment of children. Although this model is based on a group of contaminants, it opens new horizons on how environmental sciences, such as neurotoxicology and environmental epidemiology, can articulate with the theoretical models from human sciences to provide a broader approach to study the effects on human neurodevelopment.
Uma crescente literatura relata a necessidade de uma abordagem integrada para estudar os efeitos do ambiente físico no neurodesenvolvimento de crianças. A avaliação da verdadeira neurotoxicidade dos poluentes não pode ser realizada separadamente dos contextos ecológicos e multidimensionais em que atuam. Neste estudo, sob a perspectiva do modelo bioecológico de Bronfenbrenner, um modelo conceitual foi desenvolvido para abranger as características sociais e biológicas das crianças desde o período gestacional até a infância, considerando a exposição a metais tóxicos. Primeiro, apresentamos a toxicidade dos principais metais e algumas noções conceituais que utilizamos em nossa abordagem, tais como determinantes sociais e estruturais da saúde, carga alostática, incorporação e conceitos epigenéticos. Em seguida, explicamos os principais aspectos do modelo bioecológico de Bronfenbrenner, que permitem a integração da relação gene-social, além do ambiente físico, onde esses metais atuam. Por fim, apresentamos e discutimos o quadro conceitual mostrando como, na realidade, fatores biológicos e sociais podem, em conjunto, influenciar o neurodesenvolvimento das crianças. Embora esse modelo seja baseado em um grupo de contaminantes, ele abre novos horizontes sobre como as ciências ambientais, como a neurotoxicologia e a epidemiologia ambiental, podem dialogar com os modelos teóricos das ciências humanas para ter uma abordagem mais ampla ao estudar os efeitos no neurodesenvolvimento humano.
Una creciente literatura informa la necesidad de un enfoque integrado para estudiar los efectos del entorno físico en el neurodesarrollo de los niños. La evaluación de la verdadera neurotoxicidad de los contaminantes no puede llevarse a cabo por separado de los contextos ecológicos y multidimensionales en los que actúan. En este estudio, desde la perspectiva del modelo bioecológico de Bronfenbrenner, se desarrolló un modelo conceptual para abarcar las características sociales y biológicas de los niños desde el período gestacional hasta la infancia, considerando la exposición a metales tóxicos. Primero, presentamos la toxicidad de los principales metales y algunas nociones conceptuales que utilizamos en nuestro enfoque, como los determinantes sociales y estructurales de la salud, la carga alostática, la incorporación y los conceptos epigenéticos. A continuación, explicamos los principales aspectos del modelo bioecológico de Bronfenbrenner, que permiten la integración de la relación gen-social, además del entorno físico, donde actúan estos metales. Finalmente, presentamos y discutimos el marco conceptual que muestra cómo, en realidad, los factores biológicos y sociales pueden, en conjunto, influir en el neurodesarrollo de los niños. Aunque este modelo se basa en un grupo de contaminantes, abre nuevos horizontes sobre cómo las ciencias ambientales, como la neurotoxicología y la epidemiología ambiental, pueden dialogar con los modelos teóricos de las ciencias humanas para adoptar un enfoque más amplio al estudiar los efectos sobre el neurodesarrollo humano.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review of studies applying Bronfenbrenner's bioecological theory in international and intercultural education research.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1233925. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1233925. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38259539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bronfenbrenner's Bioecological Theory Revision: Moving Culture From the Macro Into the Micro.Perspect Psychol Sci. 2017 Sep;12(5):900-910. doi: 10.1177/1745691617704397. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28972838
-
Developmental Understanding of Death and Grief Among Children During COVID-19 Pandemic: Application of Bronfenbrenner's Bioecological Model.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 29;12:654584. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.654584. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34658940 Free PMC article.
-
The physical environment and child development: an international review.Int J Psychol. 2013;48(4):437-68. doi: 10.1080/00207594.2013.804190. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Int J Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23808797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Link between Animal Cruelty and Family Violence: The Bioecological Systems Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 30;17(9):3116. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093116. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32365760 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Maternal Exposure to Potentially Toxic Metals and Birth Weight: Preliminary Results from the DSAN-12M Birth Cohort in the Recôncavo Baiano, Brazil.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jun 23;20(13):6211. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20136211. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37444059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong DW, Hall KR, Hernandez LW. Counseling individuals through the lifespan. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2015.
-
- Bronfenbrenner U. The ecology of human development: experiments by nature and design. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 1979.
-
- Bronfenbrenner U, Ceci JS. Nature-nurture reconceptualized in developmental perspective a bioecological model. Psychol Rev. 1994;101:568–586. - PubMed
-
- Bronfenbrenner U, Evans GW. Developmental science in the 21st century emerging questions, theoretical models, research designs and empirical findings. Soc Dev. 2000;9:115–125.
-
- Bronfenbrenner U, Morris PA. Damon W, Lerner RM. Handbook of child psychology. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; 2007. The bioecological model of human development. pp. 739–828.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

